The Carnegie Mellon University Software Engineering Institute pioneered the world standard software development and QA (Quality Analysis) process "The Capability Maturity Model Integration (commonly referred to as CMMI or just CMM)". It can be applied to the development of most products, but CMM is most effective for software QA.
CMMI defines practices that businesses have implemented on their way to success. Practices cover topics that include collecting and managing requirements, formal decision making, measuring performance, planning work, handling risks, and more.
Using these practices, you can improve your chances of business success. CMMI practices can be used in a team, a project, a division, or an entire organization.
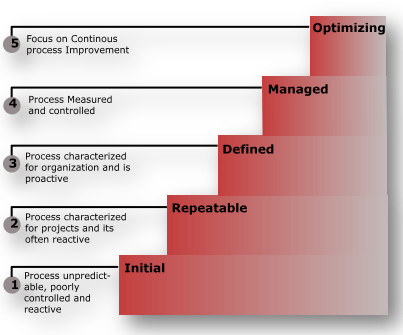
According to SEI (Software Engineering Institute) CMMI has 5 different levels i.e. from Level 1 to Level 5. I have tried to explain these levels in detail so that you can easily understand the whole process.
CMMI staged representation:

- Difference between CMM and CMMI:
CMM: - This is applicable only for software industry.
KPAs (Key Process Areas) -18
CMMI: - This is applicable for software, out sourcing and
all other industries.
KPAs (key Process Areas) – 25
- CMMI Process Areas:

CMMI Level 1: INITIAL
At maturity level 1, processes are usually ad hoc and the organization usually does not provide a stable environment. Success in these organizations depends on the competence and heroics of people in the organization and not on the use of proven processes. In spite of this ad hoc, chaotic environment, maturity level 1 organizations often produce products 387 and services that work; however, they frequently exceed the budget and schedule of their projects.
Maturity level 1 organizations are characterized by a tendency to over commit, abandon processes in the time of crisis, and not be able to repeat their past successes again.
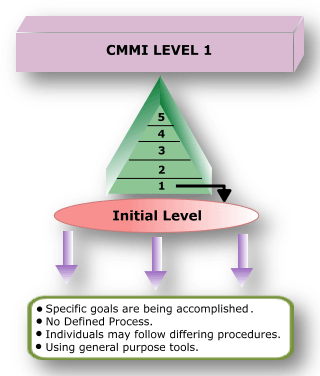
Level 1 Key Process Area: Process is informal and Adhoc.
RESULT:

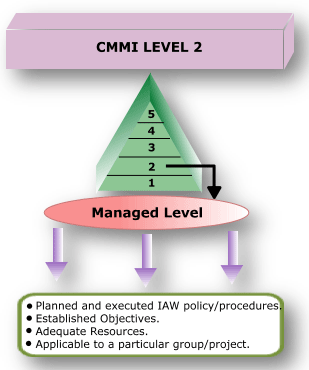
CMMI Level 2: REPEATABLE/MANAGED:
At maturity level 2, software development successes are repeatable. The processes may not repeat for all the projects in the organization. The organization may use some basic project management to track cost and schedule.
Process discipline helps ensure that existing practices are retained during times of stress. When these practices are in place, projects are performed and managed according to their documented plans.
Project status and the delivery of services are visible to management at defined points (for example, at major milestones and at the completion of major tasks).
Basic project management processes are established to track cost, schedule, and functionality. The minimum process discipline is in place to repeat earlier successes on projects with similar applications and scope. There is still a significant risk of exceeding cost and time estimates.
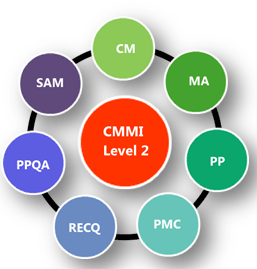
- Level 2 Key Processing Area:
RESULT:

CMMI Level 3: DEFINED
At maturity level 3, processes are well characterized and understood, and are described in standards, procedures, tools, and methods. The organization's set of standard processes, which is the basis for level 3, is established and improved over time. These standard processes are used to establish consistency across the organization. Projects establish their defined processes by the organization's set of standard processes according to tailoring guidelines. The organization's management establishes process objectives based on the organization's set of standard processes and ensures that these objectives are appropriately addressed. A critical distinction between level 2 and level 3 is the scope of standards, process descriptions, and procedures. At level 2, the standards, process descriptions, and procedures may be quite different in each specific instance of the process (for example, on a particular project). At level 3, the standards, process descriptions, and procedures for a project are tailored from the organization's set of standard processes to suit a particular project or organizational unit.
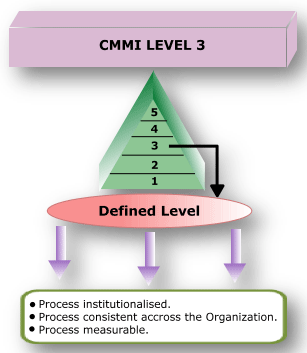
- Level 3 Key Processing Area:
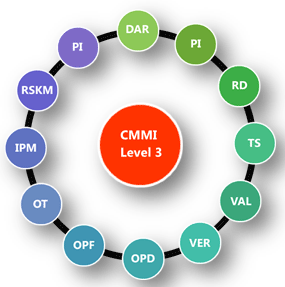
RESULT:

CMMI Level 4: QUANTATIVELY MANAGED
Using precise measurements, management can effectively control the software development effort. In particular, management can identify ways to adjust and adapt the process to particular projects without measurable losses of quality or deviations from specifications. Sub processes are selected that significantly contribute to overall process performance. These selected sub processes are controlled using statistical and other quantitative techniques. A critical distinction between maturity level 3 and maturity level 4 is the predictability of process performance. At maturity level 4, the performance of processes is controlled using statistical and other quantitative techniques, and is quantitatively predictable. At maturity level 3, processes are only qualitatively predictable.
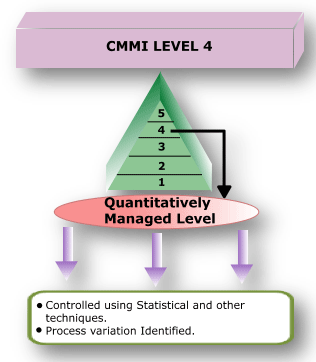
- Level 4 Key Processing Area:
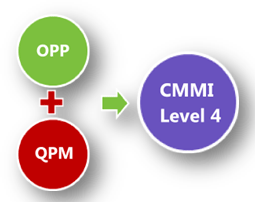
RESULT:

CMMI Level 5: OPTIMIZING
A maturity Level 5, optimizing process is a quantitatively managed process that is improved, based on an understanding of the common causes of process variation inherent in the process. It focuses on continually improving process performance through both incremental and innovative improvements. Both the defined processes and the organization's set of standard processes are targets of improvement activities.
Level 4 focuses on establishing baselines, models, and measurements for process performance. Level 5 focuses on studying performance results across the organization or entire enterprise, finding common causes of problems in how the work is done (the process used), and fixing the problems in the process. The fix would include updating the process documentation and training involved where the errors were injected.
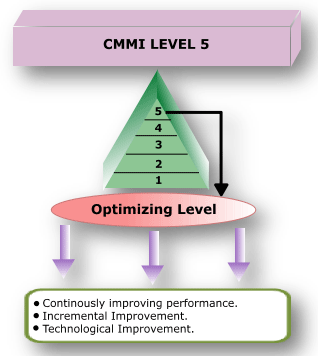
- Level 5 Key Processing Area:
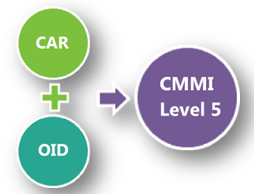
RESULT:
