Introduction
In programming languages like C and C++, we can define a variable and then accidentally use it before initializing it. C and C++ languages have no in-built feature that can recognize that being done but C# does not allow us to use an unassigned variable; this rule is known as Definite Assignment Rule. We must assign a value to a variable before using it; otherwise we will get a "compile-time" error.
Consider in C++ Language
Let's take a look at an example given below in C++ Language; it has a main method having an unassigned variable named "sampleValue" but when we run this, no error is issued. Even this display some value say it as default value.
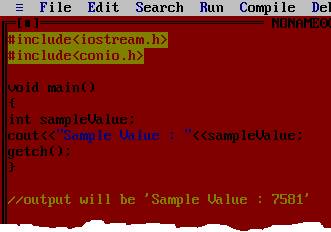
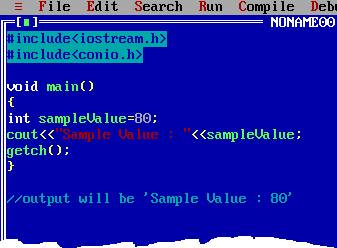
Try assigning a value in the variable "sampleValue" and look at the output, it has changed (overwritten) by the new value. Look at the image below.
Consider in C# Language
Let's take a look at the example given below in the C# Language; it has a main method having an unassigned variable named "price" but when we run this, a "compile-time error" is issued. Look at the image given below.
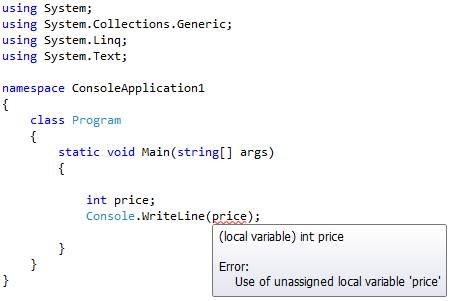
Try to assign a value to the ariable "price" and look at the output, an error is issued. Look at the image below.

So, finally at the end we have the following points.
- A variable must be definitely assigned at each location where it's value is obtained.
- A variable must be definitely assigned at each location where it is passed as a reference parameter.
- All output parameters of a function member must be definitely assigned at each location where the function member returns.
- The "this" variable of a "struct-type" instance constructor must be definitely assigned at each location where that instance constructor returns.
HAVE A HAPPY CODING!!