Creating a Web Role
In this article we are creating a web role using Visual Studio 2010. This will
make the reader familiar with Windows Azure.
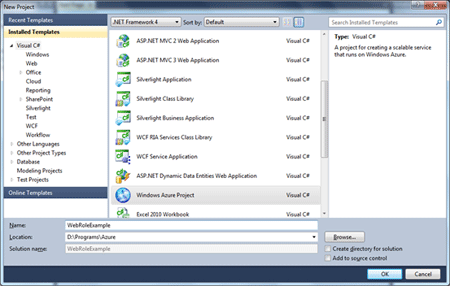
Open Visual Studio 2010 and use the command New Project. From the appearing
dialog box select the Windows Azure Project option from the Visual C# group.
Enter an appropriate name for the project and click Ok to continue. Now you will
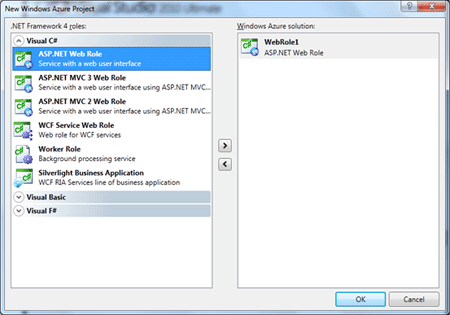
be prompted with another dialog for selecting the type of project.
Double click on the ASP.NET Web Role option to select a web role project and
click the Ok button.
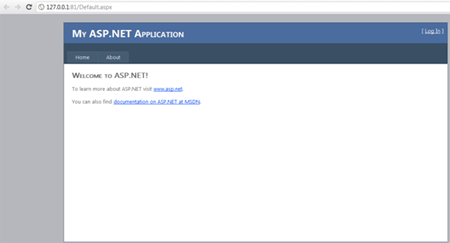
Now you are ready with the Web Role project. Now execute the application and you
will be able to see the application inside the browser. From the system tray,
you can verify the Windows Azure Emulator as running.
If successfully executed, you can see the web role opened in a browser like
below:
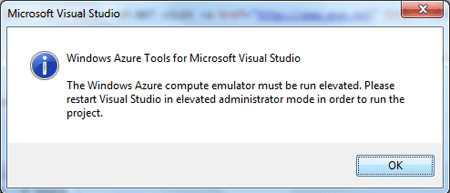
Exceptional Case 1
In case the emulator raised an error like below dialog, you have to restart
Visual Studio in the Computer Administrator context.
Exceptional Case 2
In case you are struck with issue of Compute Emulator Shutdown issue, you can
resolve it with the
link
Deploying the Web Role
After developing the web role, we have to package it and deploy to the cloud.
The entire steps in this are:
- Create Web Role
- Create Package
- Deploy to Cloud
Creating the web role is already performed. Now
we need to do the following steps.
Create Package
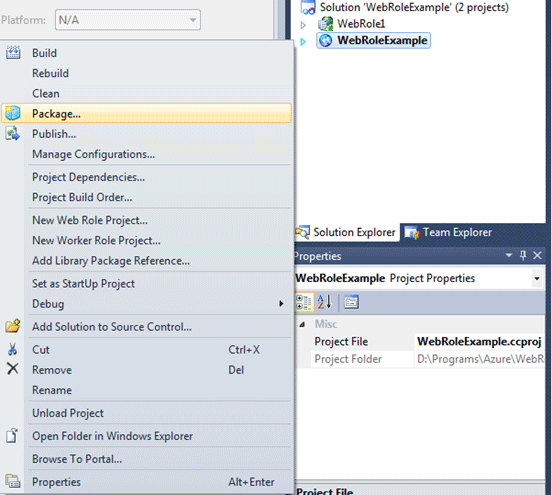
For creating the package, right click on the project context menu and click
Package.
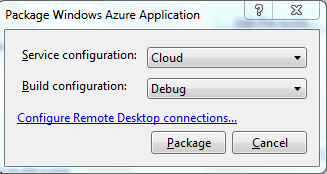
Now as dialog box will be appearing, leave the default options selected and
click the Package button on the dialog.
After performing the packaging, the folder containing package is opened in a new
explorer window automatically.
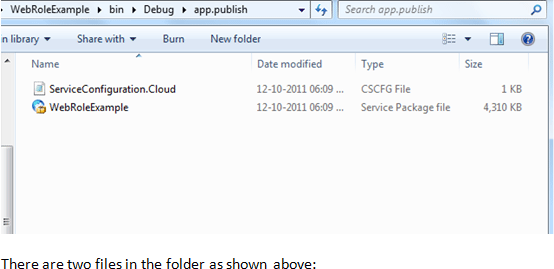
There are two files in the folder as shown above:
- Configuration File
- Service Package File
The Configuration file contains the instance
count, application setting entries etc.
Deploy to Cloud
The deploying part contains deploying the package file and the configuration
file. For deploying the files, we need to sign in to the Windows Azure Portal.
After signing in, click on the New Hosted Service button from the left top
panel. The following dialog box appears.
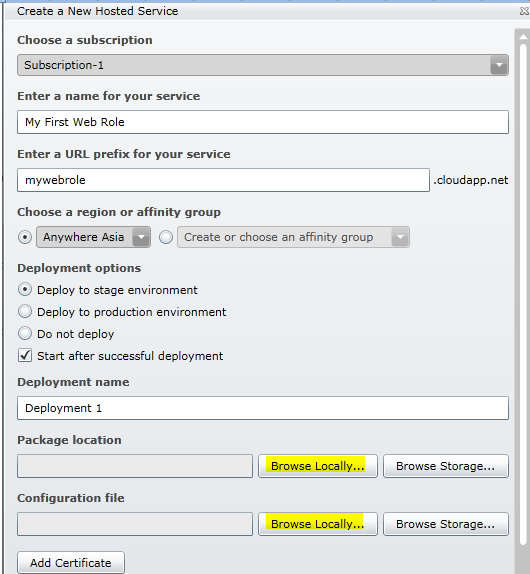
Detailing Input Fields in Dialog Box
The subscription list automatically selects the default subscription (trial).
In the service name text box, enter a name for the service.
In the service URL prefix text box, enter a unique prefix name.
In the region, select an appropriate region of deployment.
Enter an appropriate deployment name in the final text box.
Select Package
Now, we need to specify the Package location and Configuration file. Use the
Browse locally… button for these and select the files from your local machine.
After specifying all the inputs, click the Ok button. (In case of instance
warning box, click Yes to override it for time being)
Now you can see that the entry is shown as preparing to upload in the list.
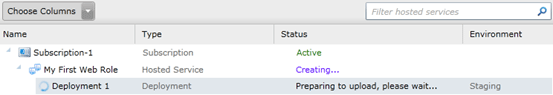
Waiting for Upload Operation
We need to wait a few minutes for the upload operation to be completed. After
the upload operation is completed the instance will be started.
After all the operations are completed the status will turn to ready as show in
the image below:
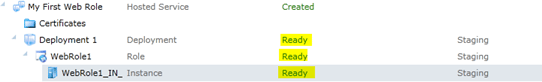
Getting the Deployed Url
For viewing the deployed web role we need to get the url. For this select the
Deployment 1 row from the list above.
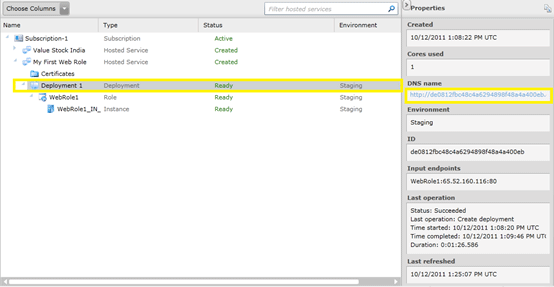
From the property pane on the right we can see the DNS name.
Viewing the Deployed Web Role
Clicking on the DNS name link from the properties the web role will get opened
in the browser as shown below (please note the staging url)
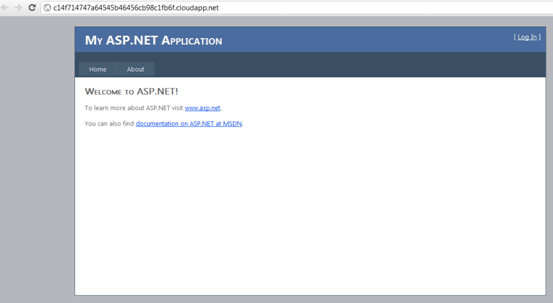
More Information
Some additional information has to be known while dealing with roles.
Virtual Machine Size
The virtual machine size provides the resource capacity of the virtual machine.
The parameters varying with virtual machine size are:
- CPU Speed
- Memory (RAM)
- Instance Storage (Hard Disk)
- I/O Performance
The sizes for virtual machine are:
- Extra Small
- Small
- Medium
- Large
- Extra Large
The cost of billing will be varying depending
on the virtual machine size.
The ServiceDefinition.csdef file can be used to specify the VM size.
<?xml
version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<ServiceDefinition
name="WebRoleExample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceDefinition">
<WebRole
name="WebRole1"
vmsize="Small">
<Sites>
<Site
name="Web">
<Bindings>
<Binding
name="Endpoint1"
endpointName="Endpoint1"
/>
</Bindings>
</Site>
</Sites>
<Endpoints>
<InputEndpoint
name="Endpoint1"
protocol="http"
port="80"
/>
</Endpoints>
<Imports>
<Import
moduleName="Diagnostics"
/>
</Imports>
</WebRole>
</ServiceDefinition>
Instance Count
The number of instances of the Web Role can be specified using the instance
count option. The number of instances will be managed by a Load Balancer
automatically by the cloud.
The ServiceConfiguration.cscfg file can be used to specify the instance count.
<?xml
version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<ServiceConfiguration
serviceName="WebRoleExample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceConfiguration"
osFamily="1"
osVersion="*">
<Role
name="WebRole1">
<Instances
count="1"
/>
<ConfigurationSettings>
<Setting
name="Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Plugins.Diagnostics.ConnectionString"
value="UseDevelopmentStorage=true"
/>
</ConfigurationSettings>
</Role>
</ServiceConfiguration>
Locating the files
From the solution explorer we can locate the files as shown below:
Summary
In this article we have seen how to create and deploy a web role in Windows
Azure.