SQL SELECT DISTINCT Statement
Introduction
In this chapter, we will learn about the basics of the SQL SELECT DISTINCT statement
SELECT SQL DISTINCT Statement
The SELECT DISTINCT statement is used to return only distinct
(different) values.
The SELECT DISTINCT eliminates duplicate records from results
SELECT DISTINCT can be used with aggregates: COUNT, AVG, MAX, etc
SELECT DISTINCT operators on a single column DISTINCT for multiple columns is not supported
SQL DISTINCT keyword is used in conjunction with the SELECT statement to eliminate all the duplicate records and fetching only unique records
There may be a situation when you have multiple duplicate records in a table. while fetching such records, it makes more sense to fetch only those unique records instead of fetching duplicate records
Inside a table, a column often contains many duplicate values, and sometimes you
only want to list the different (distinct) values
Syntax
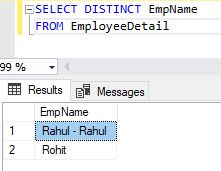
- SELECT DISTINCT Emp_Name
- FROM EmployeeDetail;
Example
SELECT COUNT DISTINCT statement
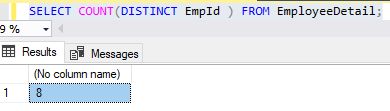
The SELECT DISTINCT COUNT() function returns the number of rows that matches a specified criteria
The following SQL statement lists the number of different (DISTINCT)EmployeeDetails EmpId
Syntax
- SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT EmpId) FROM EmpDetail;
SELECT AVG DISTINCT statement
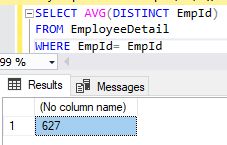
The AVG DISTINCT () function returns the average value of a numeric column
The following SQL statement lists the number of different (DISTINCT)EmployeeDetails EmpId
Syntax
- SELECT AVG(DISTINCT EmpId)
- FROM EmployeeDetail
- WHERE EmpId= EmpId
Example
SELECT MAX DISTINCT statement
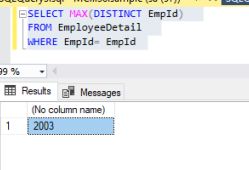
The SELECT MAX DISTINCT function returns the largest value of the selected column
Syntax
- SELECT MAX(DISTINCT EmpId)
- FROM EmployeeDetail
- WHERE EmpId= EmpId
Example
NOTE
This example above will not work in Firefox and Microsoft edge! Because COUNT(DISTINCT column_name) is not supported in Microsoft access databases Firefox and Microsoft Edge is using Microsoft access in our examples.
Here is the workaround for ms access.
SQL SELECT DISTINCT on multiple columns
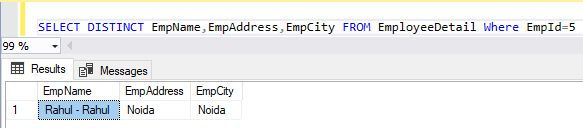
Here is a simple Example on some selected columns in EmpoyeeDetail table where EmpId= 5
Syntax
- SELECT DISTINCT EmpName,EmpAddress,EmpCity FROM EmployeeDetail Where EmpId=5
Example
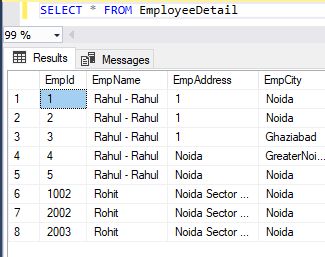
SELECT example without DISTINCT
The following SQL statement selects all (including the duplicates) values from the EmpName column in the EmployeeDetail table
Syntax
- SELECT * FROM EmployeeDetail
Example
Summary
In the next chapter, we will learn the basics of the SQL TOP statement.
Author
Naresh Beniwal
Tech Writter
7.1k
1.9m
