Types of Virtual Networks
Virtual networking is analogous to traditional physical networking; still, in virtual networking, some or all of the tackle factors are replaced with virtual network factors comprised of software. This eliminates the need to configure physical tackle factors physically. Virtual network factors can be configured more fluently than physical factors, allowing the networking of virtual machines to be managed with lesser ease and inflexibility.
Virtual machines must be connected to a virtual network element, and that virtual element must have access to the physical network. There are several ways the virtualized factors can be connected to a physical network in order to allow VMs to communicate with each other and with other biases. This section explores the 3 network types used to set up VMs with a connection.
Bridged Network
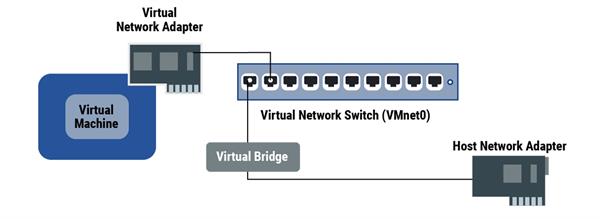
A bridged network is a network type where both a virtual machine and the host that it's running on are connected to the same network. Bridged networking connects a virtual machine to the network using the host computer's Ethernet appendage. The network used by the host is the main public network, which is generally appertained to as “ the internet ”. This is possible because the host shares its IP address with the Virtual Machine.
With bridged networking, the virtual network appendage( vnic) in the virtual machine connects to a physical network appendage( NIC) in the host system. The host network appendage enables the virtual machine to connect to the LAN( Original Area Network) that the host system uses. Bridged networking works with both wired and wireless host network appendages.
Note
Bridged networking configures the virtual machine as a unique identity on the network, separate from and unconnected to the host system. The virtual machine is a full party in the network. It has access to other machines on the network, and other machines on the network can communicate with it as if it were a physical computer on the network.
NAT Network
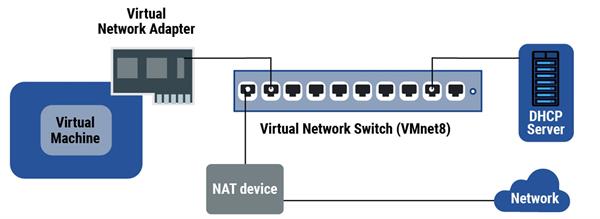
NAT( Network Address restatement) takes an IP address and translates it into another IP address. On a NAT network, a virtual machine doesn't have its own IP address on the external network. rather, a separate private network is set up on the host computer.
NAT is useful when you have a limited force of IP addresses. NAT works by rephrasing addresses of virtual machines in a private network called a VMnet to that of the host machine. When a virtual machine sends a request to pierce a network resource, to the network resource it appears as if the request came from the host machine.
The NAT device on the network translates the information going to the host's public IP address and forwards it to the private IP address for the Virtual Machines.
The VMnet is suitable to connect to the public external network using the restated IP addresses enabled by a point called harborage forwarding. Port forwarding allows incoming web business to pass through a specific harborage, chosen by the director, to the internal network.
Incoming network business is transmitted in the form of data packets. The NAT device is suitable to sort the packets intended for each virtual machine and sends them to the correct destination. A data packet contains a unit of data, information about the network it's traveling on, and where it's going. When a packet doesn't reach its destination, this is called packet loss.
The topology of a NAT network involves a Virtual Machine connected to a virtual network interface card( vnic) which allows it to connect to the virtual switch( vswitch). The vswitch is also connected to a NAT device that translates the IP addresses and allows harborage forwarding to connect to the external network.
Consider This
In the dereliction configuration, virtual machines get an address on this private network from the virtual DHCP garçon. DHCP is an acronym for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. A DHCP garçon is a system that uses the DHCP protocol to assign IP addresses to the bias on the network.
Host-only Network
Host-only networking creates a private internal network for the VMs to connect to, analogous to a NAT network. still, without IP address restatement, the VMs can only stay in the private network and don't have direct access to the public external network.
Host-only networking provides a network connection between the virtual machine and the host computer, using a virtual Ethernet appendage( vnic) that's visible to the host operating system. This approach can be useful if you need to set up an insulated virtual network.
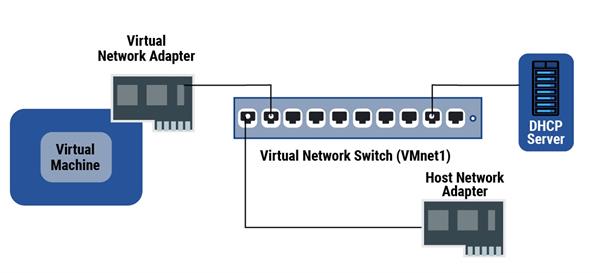
Still, your virtual machine and the host virtual appendage are connected to a private Ethernet network, If you use host-only networking. Addresses on this type of network are also handled by a DHCP garçon.