Self Hosting in WCF Application
Introduction
In this series, we are explaining all about WCF. The previous few chapters explained various important concepts of WCF applications. You can read them here:
In this chapter, we will learn to host WCF applications in a self-hosting environment. As we know, WCF is the next and updated solution of Web Services and one basic difference between them is, it's a hosting environment. We can host a Web Service only in an IIS server and consume it by HTTP protocol. WCF leverages the limitation, we can host a WCF service in various environments. So, let's see what are the possible ways to host a WCF service.
Various WCF hosting environments
The following are the various hosting environments:
- Self-hosting
- IIS server
- Windows Activation Server (WAS)
Ok, so there are three different environments for WCF services. But the most popular environment in the IIS server and the next choice is to self-hosting. We can say that 70% of services run in the IIS server, 25% runs self-hosted and the remaining are hosted in WAS.
What WCF Self-Hosting is?
Let's learn the concept of Self-Hosting. The single line answer is "It hosts with the same solution". What does that mean? It means that we have our project (it may be Windows or a web application or something else) and we want to host one WCF service within this solution locally. This type of hosting is called Self-Hosting. To implement self-hosting we need to include System.Service.Model.ServiceHost namespace that we will see in the example.
Let's implement a self-hosting example step-by-step.
We will now implement the self-hosting example step-by-step. Please follow it.
Step 1: Create a console application.
As we said, self-hosting can be done in any type of application; we will implement self-hosting in the console application.
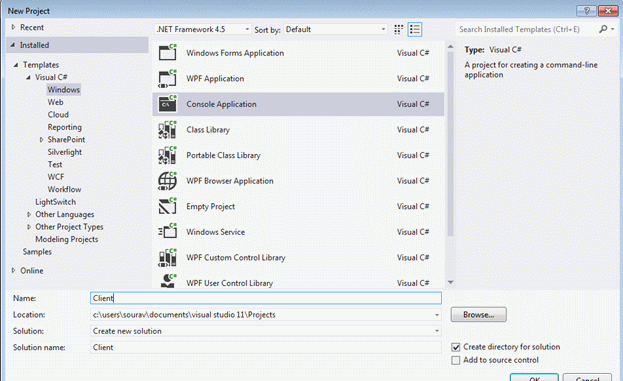
We have given the name "client" to this console application. Now proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Add the System.ServiceModel.dll to the project.
This is our next step, go to Solution Explorer and right-click on References then select "Add references" then add a reference for "System.ServiceModel".
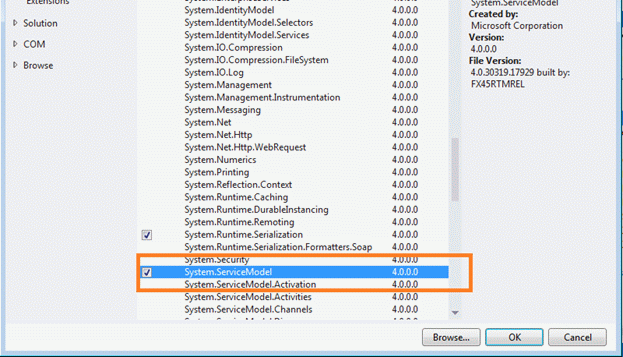
Once you click on "OK" the reference will be added to your solution. So, click "OK" and go to the next step.
Step 3: Add one interface to the solution.
As we know in WCF we need to implement a ServiceContract, so we need to define the interface. Add one interface to the solution.
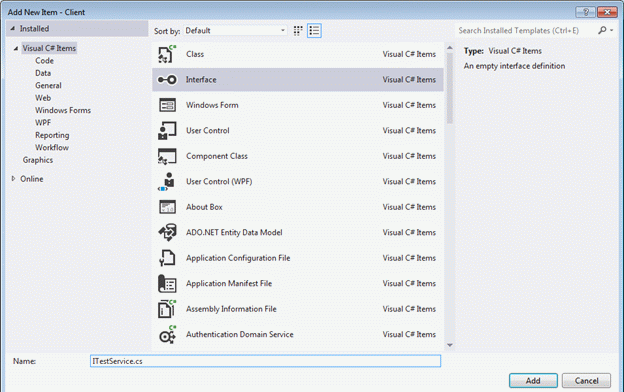
Step 4: Add the following code to the interface.
Now we will declare the methods in the interface. Here is a simple code.
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace Client
- {
- [ServiceContract]
- interface ITestService
- {
- [OperationContract]
- String WelcomeUser(String name);
- }
- }
Step 5: Add one class into the solution.
Since we need to implement the interface above, we will include one class file and we will get it done. So, add a class file to the solution.
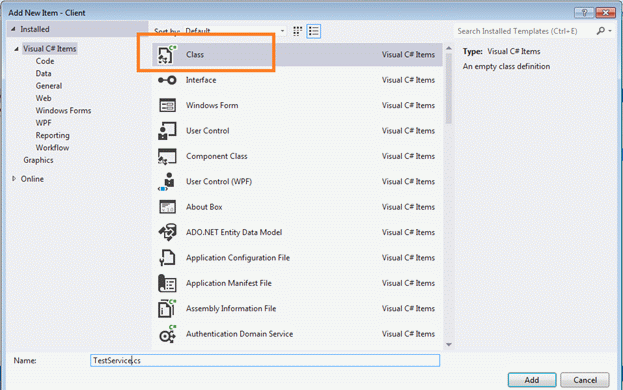
Add the following code to our class:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace Client
- {
- public class TestService : ITestService
- {
- public String WelcomeUser(String name)
- {
- return String.Format("Welcome " + name);
- }
- }
- }
Step 6: Open the Main() function of the application and modify the code.
Our service is now set up and we need to host the service. To host the service we need to open the Program class (the default in a console app) and modify the code like below.
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Diagnostics;
- using System.Collections;
- using Client;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- using System.ServiceModel.Description;
- namespace Client
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Uri baseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:6525/TestService");
- using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(Client.TestService), baseAddress))
- {
- ServiceMetadataBehavior smb = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
- smb.HttpGetEnabled = true;
- smb.MetadataExporter.PolicyVersion = PolicyVersion.Policy15;
- host.Description.Behaviors.Add(smb);
- host.Open();
- Console.WriteLine("The service is ready at: {0}", baseAddress);
- Console.WriteLine("Press <Enter> to stop the service");
- Console.ReadKey();
- host.Close();
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
- }
Step 7: Run the application.
This is the last step to host the service. Press F5 now and run the application. Here is the output. We see that the service is hosted in the same URL.
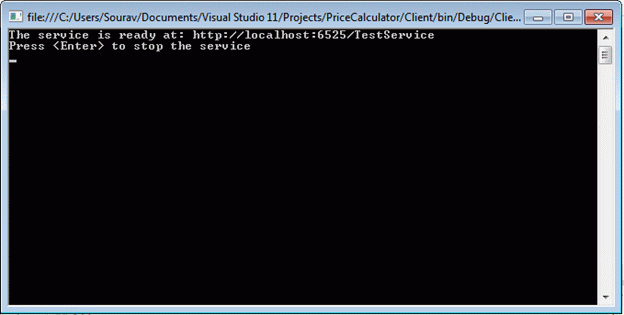
Note: If you get the error "Assembly cannot read blab bla" then please run the Visual Studio in Administrator mode (I have spent much time solving the issue).
Conclusion
In this step-by-step chapter, we have learned to host a WCF service in a Self-Hosting environment. Hope you have learned it. In a future chapter, we will dig more into this subject (WCF).