Function Overloading in WCF Application
Introduction
In this series, we are talking about WCF applications. Previous chapters explained a few important concepts of WCF applications. You can read the full series here:
In this part, we will learn the concepts of function overloading in WCF applications. I hope you are familiar with the concept of function overloading, but the concept of function overloading in .NET is a little different in WCF applications. In traditional .NET applications (read Windows app or Web app) we can implement the concept of function overloading by passing various types of parameters where the function name should be the same.
Try to understand the following example.
Code for the service contract
This is the code for the service contract (interface implementation). Try to understand that we have been given the same attribute ("[OperationContract]") in both function declarations.
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Runtime.Serialization;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- using System.ServiceModel.Web;
- using System.Text;
- namespace WCF
- {
- [ServiceContract]
- public interface IService1
- {
- [OperationContract]
- string AddName(string Name, string LastName);
- [OperationContract]
- string AddName(string Name, string MiddleName, string LastName);
- }
- }
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Runtime.Serialization;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- using System.ServiceModel.Web;
- using System.Text;
- namespace WCF
- {
- public class Service1 : IService1
- {
- public string AddName(string Name, string LastName)
- {
- return Name + LastName;
- }
- public string AddName(string Name, string MiddleName, string LastName)
- {
- return Name + MiddleName + LastName;
- }
- }
- }
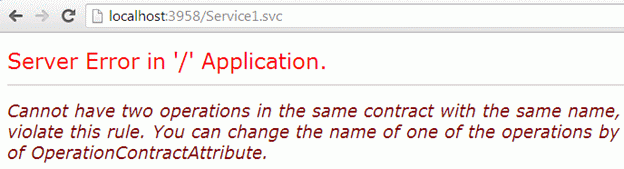
Here is the sample output. We see that it throws an exception. The reason is we cannot use the same name in a function in a WCF application.
How to implement Operator overloading
We can implement Operator overloading by specifying the proper attribute in the operation contract (within an interface). Try to understand the following example.
The following is a modified version of the Service contract.
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Runtime.Serialization;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- using System.ServiceModel.Web;
- using System.Text;
- namespace WCF
- {
- [ServiceContract]
- public interface IService1
- {
- [OperationContract(Name = "NameSurname")]
- string AddName(string Name, string LastName);
- [OperationContract(Name = "NameMiddleNameSurname")]
- string AddName(string Name, string MiddleName, string LastName);
- }
- }
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Runtime.Serialization;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- using System.ServiceModel.Web;
- using System.Text;
- namespace WCF
- {
- public class Service1 : IService1
- {
- public string AddName(string Name, string LastName)
- {
- return Name + LastName;
- }
- public string AddName(string Name, string MiddleName, string LastName)
- {
- return Name + MiddleName + LastName;
- }
- }
- }
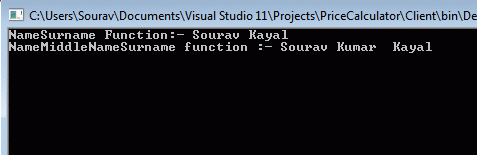
We will now implement one simple client code to consume the service. Here we have created one sample console application and consumes the service.
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Diagnostics;
- using System.Collections;
- using Client;
- using System.ServiceModel;
- namespace Client
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Client.ServiceReference1.Service1Client obj = new ServiceReference1.Service1Client();
- string name = obj.NameSurname("Sourav", " Kayal");
- Console.WriteLine("NameSurname Function:- " + name);
- name = obj.NameMiddleNameSurname("Sourav ", "Kumar " , " Kayal");
- Console.WriteLine("NameMiddleNameSurname function :- " + name);
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
Conclusion
In this quick chapter, we learned to implement function overloading in WCF applications. Hope you have understood the concept. In a future chapter, we will concentrate more on WCF.