Python For Loop
Introduction
Python For Loop
Syntax
- for IterationalVariable in sequence:
- Body of the loop
In Python, for loop works like C# foreach loop.
For loop with a list
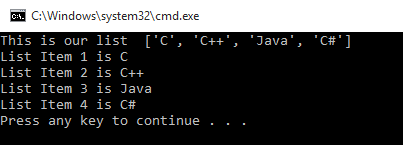
- list=['C','C++','Java','C#']
- print("This is our list ",list)
- i=1
- for val in list:
- print("List Item",i,"is",val)
- i=i+1
Output
For loop with tuple
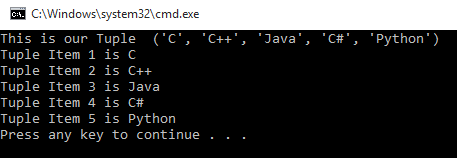
- tuple=('C','C++','Java','C#','Python')
- print("This is our Tuple ",tuple)
- i=1
- for val in tuple:
- print("Tuple Item",i,"is",val)
- i=i+1
Output

For loop with string
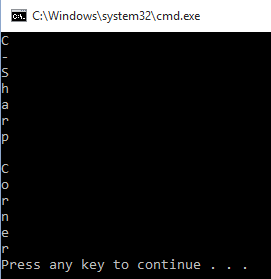
- string="C-Sharp Corner"
- for val in string:
- print(val)
Range Function
- range([start],end,[step])
- start- This is an optional argument. This argument decides from where you want to start your loop. If you do not provide this value then its value will be zero(0) by default.
- end- This argument decides the end of the loop.
- step- How much you want to increment after one iteration. This is also an optional argument. So if you do not give this argument then it will increment by 1 step.
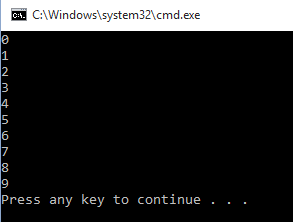
Example 1
- for val in range(11):
- print(val)
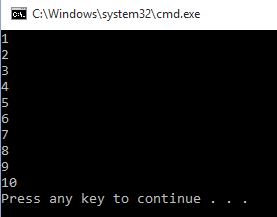
- for val in range(1,11):
- print(val)
Example 3
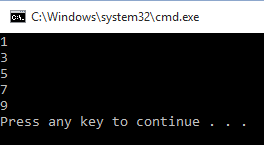
- for val in range(1,11,2):
- print(val)
For loop with else condition
else part will only execute when for loop condition will be false. If for loop will be terminated by break statement then for loop's else part never executes.
Example
- #program to check
- #weather the given number is
- #prime number or not
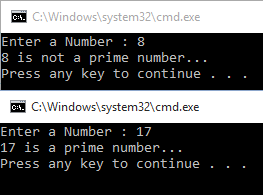
- num = int(input("Enter a Number : "))
- for i in range(2,num):
- if(num%i==0):
- print("%d is not a prime number..."%num)
- break
- else:
- print("%d is a prime number..."%num)
Nested Loop
Example 1
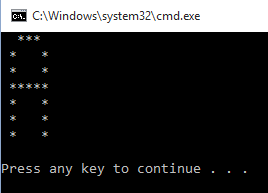
- str="";
- for Row in range(0,7):
- for Col in range(0,7):
- if (((Col == 1 or Col == 5) and Row != 0) or ((Row == 0 or Row == 3) and (Col > 1 and Col < 5))):
- str=str+"*"
- else:
- str=str+" "
- str=str+"\n"
- print(str);
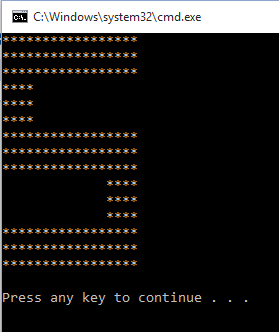
Example 2
- str="";
- for Row in range(0,7):
- for Col in range(0,7):
- if (Col == 1 or ((Row == 0 or Row == 3 or Row == 6) and (Col < 5 and Col > 1)) or (Col == 5 and (Row != 0 and Row != 3 and Row != 6))) :
- str=str+"*"
- else:
- str=str+" "
- str=str+"\n"
- print(str);
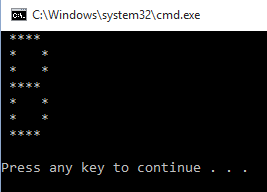
Example 3
- row=15
- col=18
- str=""
- for i in range(1,row+1):
- if((i<=3)or(i>=7 and i<=9)or(i>=13 and i<=15)):
- for j in range(1,col):
- str=str+"*"
- str=str+"\n"
- elif(i>=4 and i<=6):
- for j in range(1,5):
- str=str+"*"
- str=str+"\n"
- else:
- for j in range(1,14):
- str=str+" "
- for j in range(1,5):
- str=str+"*"
- str=str+"\n"
- print(str)
Summary
In the next chapter, you will learn how to use Python functions.
Author
Sourabh Somani
Tech Writter
47.6k
10.9m
