File Handling In Python
Introduction
In this chapter, you will learn about file handling in Python.
File handling
File handling has some functions for creating, reading, updating, and deleting files.
In Python, open () two parameters. One parameter is reporting name and any other parameter is the mode. There are four forms of mode. There are:
- “r” =read () is used for reading the file.
- “a” =append () is used to append the file (append mode)
- “w” =write () is used to write the file (write mode)
- “r+” ==read () and write () mode are used in the file handling.
- “t” - t is a text mode
- “b” - b is binary mode
Syntax
- f=open(“filename.txt”)
(or)
- f=open(“filename.txt”,“rt”)
Both are same because “r” is the default mode and read mode, “t” is the default mode and text mode
Open file and read mode
To open the file used keyword open (). The read () method for reading the file.
Example
- f=open("F:/download surya/demo.txt","r") #file name and mode
- print(f.read())# read mode
Output
Simple read mode program.
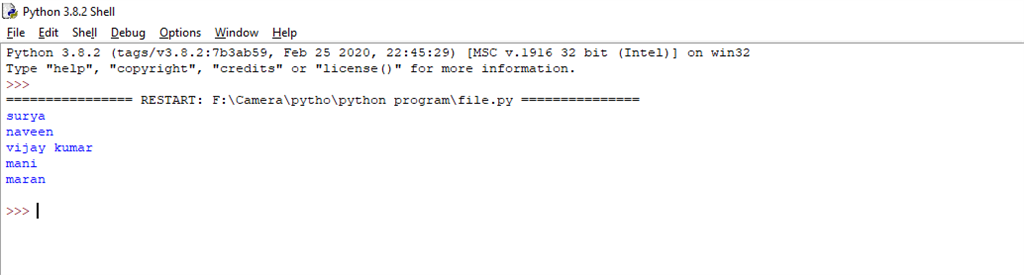
Read-only part of the File
In Python, the read method returns the whole text. We can also specify how many letters you want to return.
Example
- f=open("F:/download surya/demo.txt","r") #file name and mode
- print(f.read(2)) # how many letters you want to return.
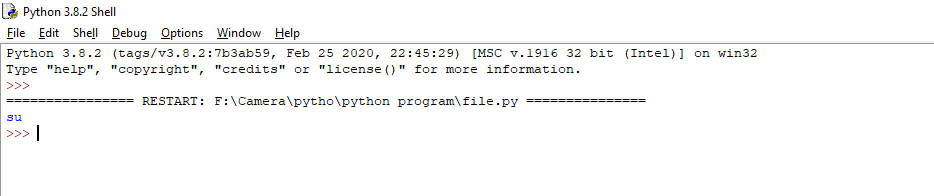
Output
Return the first 2 letters in the file.
Read lines
In python, we can return first (or) one line by using the readline() method keyword.
Example
- f=open("F:/download surya/demo.txt","r")#read mode
- print(f.readline())#Return first line in the output screen.
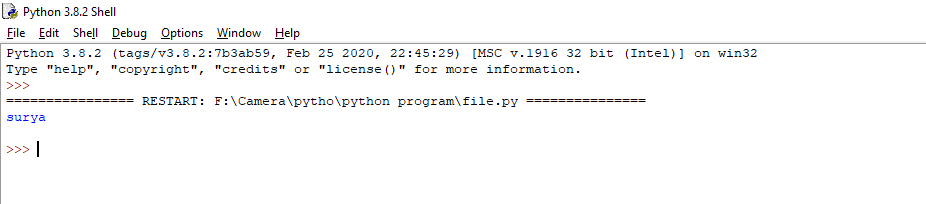
Output
Return one line in the output screen.
Loop in file
In Python, looping through the lines of the file, we can read the whole file, one by one.
Example
- f=open("F:/download surya/demo.txt","r")#read mode
- for x in f:# Return the file one by one.
- print(x)
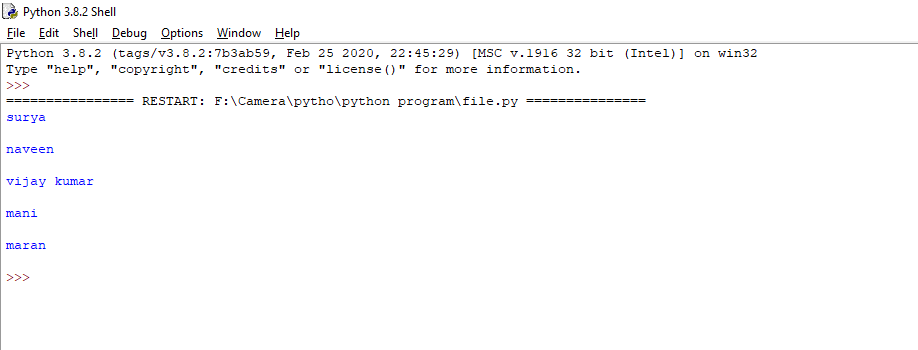
Output
Return the file one by one.
Close files
In Python, we want to close the file when you complete the work using the close() method keyword.
Example
- f=open("F:/download surya/demo.txt","r")#read mode
- print(f.read())
- f.close()# close() method is to close the file
Output
Close the file when you are finished with your work.
Conclusion
In the next chapter, we will discuss OOPs concepts.
Author
Surya S
386
3.6k
679.8k
