MongoDB Find Method (Day 7)
Before reading this article, I highly recommend reading the following previous parts of the series:
- MongoDB - Day 1 (Introduction To MongoDB)
- MongoDB - Day 2 (Install MongoDB in Windows)
- MongoDB - Day 3 (Database Basics)
- MongoDB - Day 4 (Basics of Collection)
- MongoDB - Day 5 (Data Types in MongoDB)
- MongoDB - Day 6 (Insert Method)
In the previous article, we learned about the insert method. Today, we will learn about the find method of MongoDB databases. In a relational database, we use a “Select * From Table_Name” query to fetch the data from a table. However, we use the “find” method in MongoDB to retrieve data from a collection. The find method contains many properties and options, so we can't understand the find method in a single article. Therefore, I divided this method into two parts. Today, we learn some basic operations of the find method.
Find: The find method selects documents from a collection and returns a cursor to the selected documents.
Syntax: db.Collection_Name.find( query , projection ).
Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| Query | Document | Specifies selection criteria. It is optional parameter. If not specified then it returns all records. |
| Projection | Document | Specifies fields to return . It is an optional parameter. If not specified then it returns all fields. |
The find method does its work in the following 3 steps:
- The first select documents the match query criteria.
- Select specific fields from the documents according to a projection parameter
- Returns a cursor to the selected and filtered documents
Actually, the find method returns a cursor to selected documents. This cursor automatically displays 20 records on the screen. We can use its command to continue the iteration.
First, we create a collection and insert some data into the collection. Then we retrieve these records using the find method.
Create a collection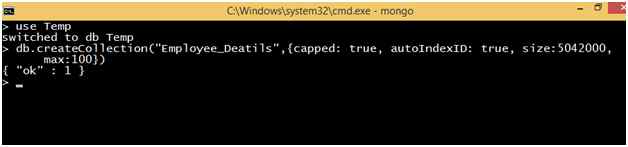
Now insert some data into the preceding collection, as in the following: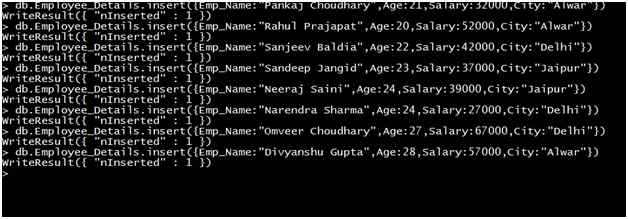
In the Employee_Details collection, we insert 8 records (documents). Now we retrieve these records using the find method in various forms.
Find() Method
The find method will display all the records of the collection in an unstructured format.
Syntax: db.Collection_Name.find()
Example: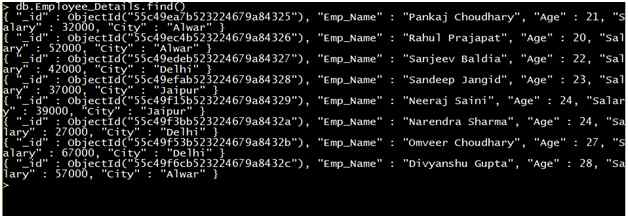
We can see that the find method returns data in a non-structured manner. That is very hard to read. Therefore, we can use the pretty() method to show the data in a structured manner.
Pretty() Method
The Pretty method shows data in a structured (formatted) manner.
Syntax: db.Collection_Name.find().pretty()
Example: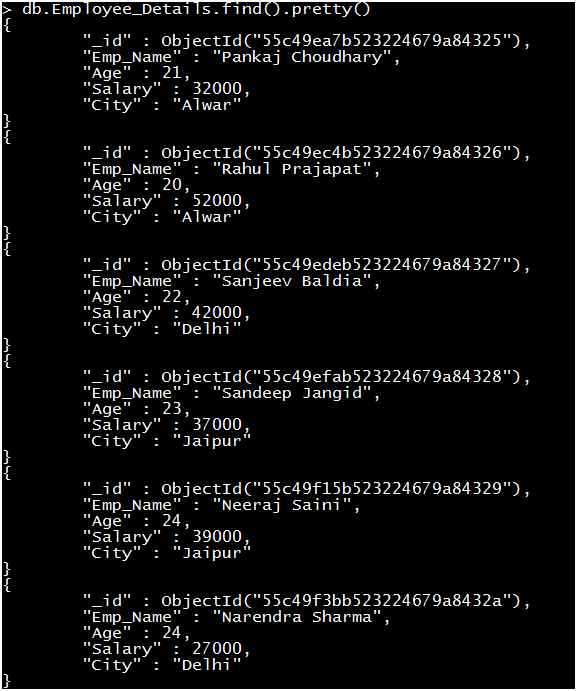
Now the preceding output is very easy to read and understand.
Find method with Conditional operators
Similar to a relational database, MongoDB supports conditional select operations. MongoDB supports a number of conditional operators. Some commonly used conditional operators are the following:
| Operator | Syntax |
| Equal | { <Key> : <Value> } |
| Less Than | { <Key> : { $lt : <value> } } |
| Greater Than | { <Key> : { $gt : <Value> } } |
| Less Than Equal | { <Key> : { $lte : <Value> } } |
| Greater Than Equal | { <Key> : { $gte : <Value> } } |
| Not Equal | { <Key> : { $ne : <Value> } } |
Now we execute some query for each conditional operator.
Query 1: Retrieve the record of all employees where City is equal to Delhi.
Output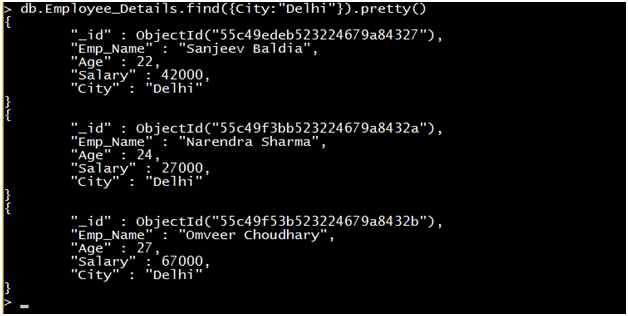
Query 2: Retrieve the record of all Employees where the age of the employee is less than 23.
Output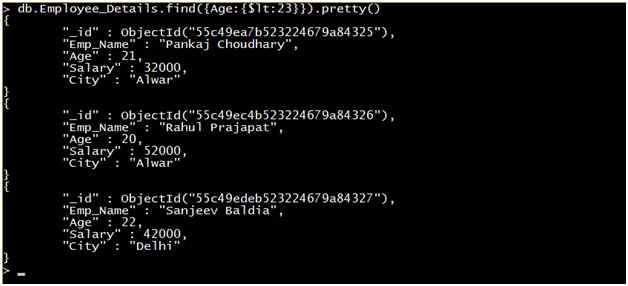
Query 3: Retrieve the record of all Employees where the Salary of the employee is greater than 40000.
Output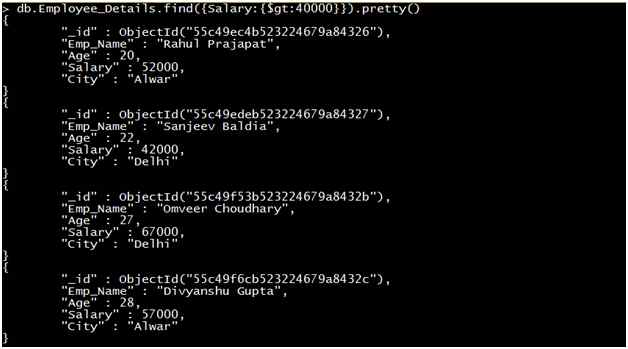
Query 4: Retrieve the record of all Employees where the age of the employee is greater than or equal to 24.
Output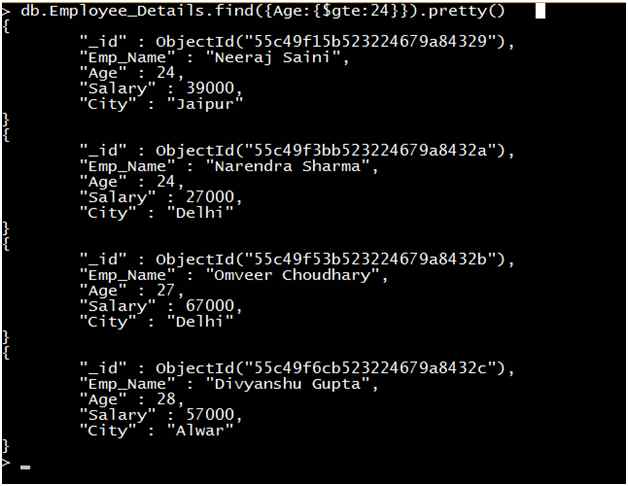
Query 5: Retrieve the record of all Employees where the Salary of the employee is less than or equal to 39000.
Output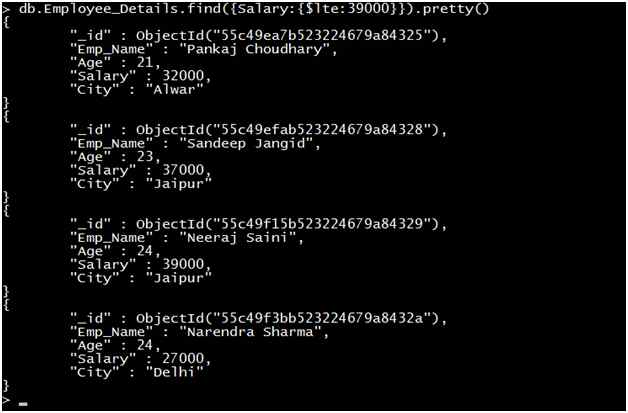
Query 6: Retrieve the record of all employees where the City of the Employee is not equal to Delhi.
Output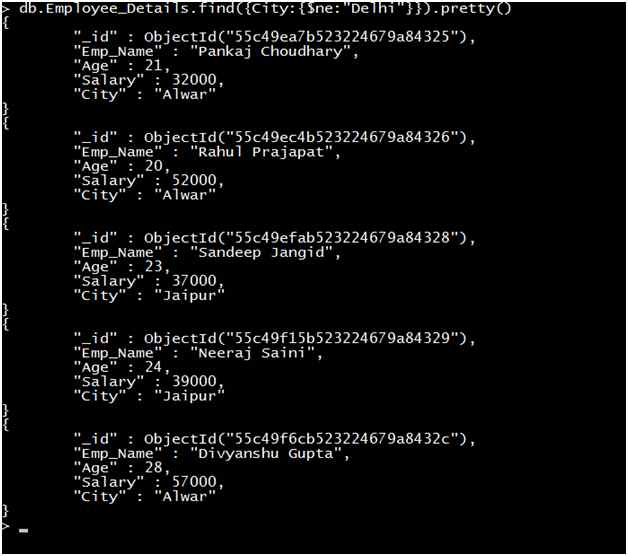
Find Method with Multiple Conditional operators
Sometimes, we must apply multiple conditional operators in a find method. MongoDB provides various methods for such requirements. Next, we will explain some of these methods.
AND Condition
Using an AND condition, we can apply multiple conditional operators. The result will be to retrieve when all the conditions become True. We can pass multiple keys by separating them with a ','. Then MongoDB treats it as an AND condition.
Syntax: db.Collection_Name.find( {Key1:Value1 , Key2:value2,……..Keyn:Valuen })
Query: Retrieve the record of all employees where the City of the Employee is not equal to Delhi and the salary is greater than 45000.
Output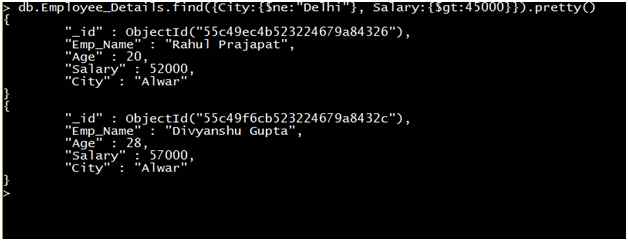
OR Condition
Using an OR condition we can apply multiple conditional operators. The result will be retrieved when one or more conditions are True. We need to use the $or keyword for an OR condition.
Syntax: db.Collection_Name.find ( { $or:[ { Key1: Value1 }, {Key2:Value2}, ……..{ Key2: Value2} ] } )
Query: Retrieve the record of all employees where the age of the Employee is greater than 25 or the salary is greater than 45000.
Output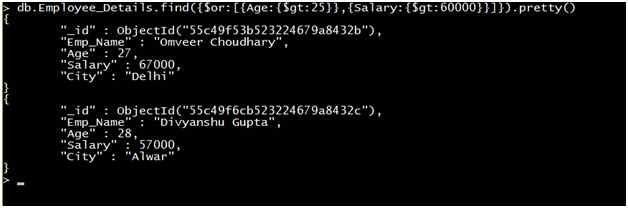
In Condition
The In condition is similar to the in condition of relational databases. The In condition is useful when we want to specify more than one value for a single key. We need to use the $in keyword for an In condition. We can retrieve the same result using the OR conditional operator that we retrieve using the $in keyword.
Query: Retrieve the record of all employees where the age of the Employee is equal to 23 or 27.
First, we retrieve the result using an OR conditional operator.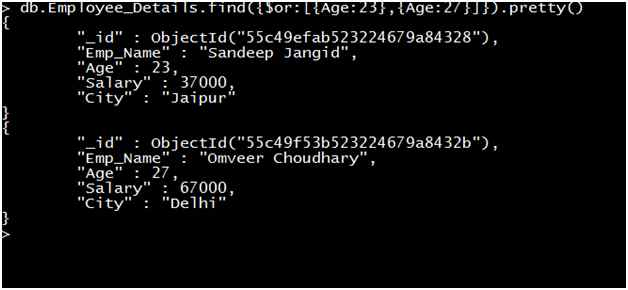
Now we retrieve the same result using an IN operator.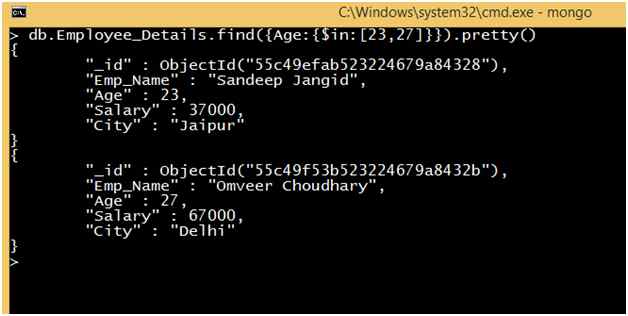
We can see that the output of both queries are the same.
Use AND and OR operator together
The following example shows a demo of how to use AND and OR conditional operators together.
Query: Retrieve the record of all employees where the Salary of the employee is greater than 50000 and the age of the Employee is equal to 23 or 27.
Output: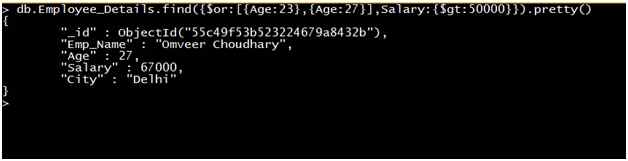
Using the AND and IN operators together
The following example shows a demo of how to use the AND and IN operators together.
Query: Retrieve the record of all employees where the city of the employee is not equal to Delhi and the age of the Employee is equal to 23 or 27.
Output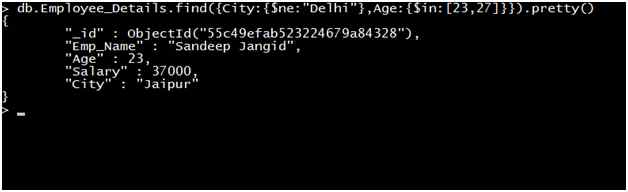
Today, we learned the find method and the use of conditional operators with the find method. In the next article, we learn some more about the find method.
