Conditional Statements In JavaScript
Introduction
In the previous chapter, we learned about Operators in JavaScript, types of operators, and how to use operators in JavaScript with example programs.
In this chapter, we will learn about Conditional Statements in JavaScript. These statements are also called Selection Statements.
The Conditional Statements in JavaScript:
- If Statement
- If Else Statement
- Elseif Statement
- Switch Case Statement
If Statement
If Statements are used for the purpose of decision making; they evaluate the statement if the condition is true. To check if the given 'If condition' is satisfied, 'If Statement' is executed; otherwise the condition is false to exit the If condition.
Syntax
- If (condition)
- {
- Statement; //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
Example
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>if Condition</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Conditional Statement in JavaScript</h1>
- <script type="text/javascript">
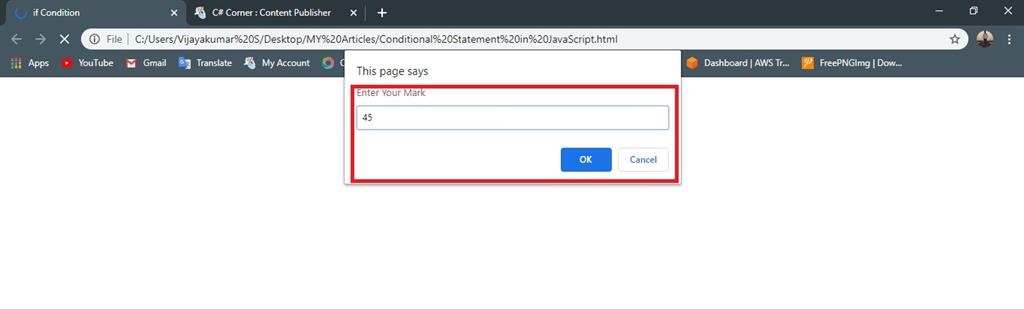
- var percentage =(prompt("Enter Your Mark"))
- if (percentage >= 40)
- {
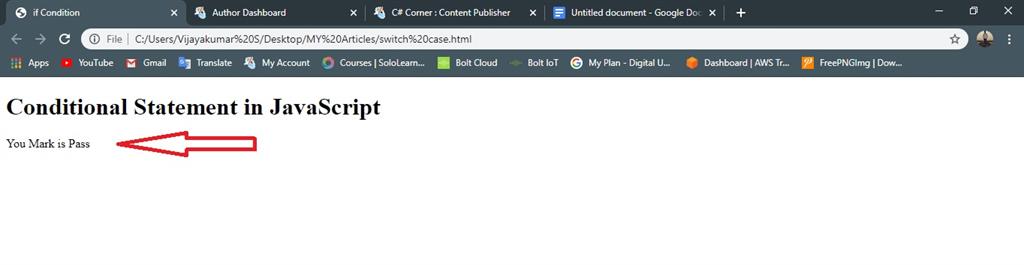
- document.write("You Mark is Pass"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
Output
If else Statement
'If else Statement' is an improvement over if Statement. It evaluates the statement if the condition is true or false. In this statement, the given 'If condition' is true means to execute the 'if Statement'. On the other hand, if the condition is false it means to execute another block.
Syntax
- if (Condition)
- {
- Statement; //true
- }
- else
- {
- Statement; //false
- }
Example
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>if Condition</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Conditional Statement in JavaScript</h1>
- <script type="text/javascript">
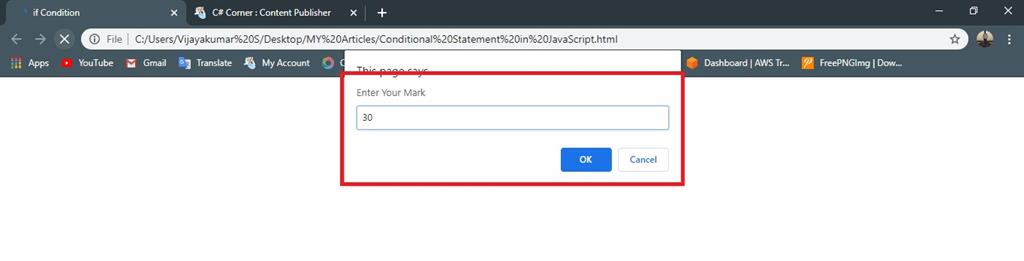
- var percentage =(prompt("Enter Your Mark"))
- if (percentage >= 40)
- {
- document.write("You Mark is Pass"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
- else
- {
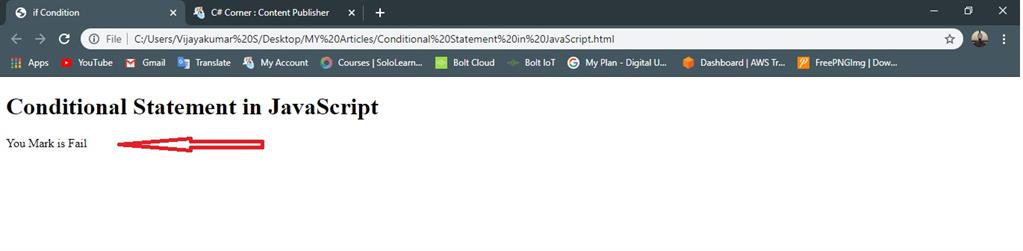
- document.write("You Mark is Fail"); //given condition is false execute the statement
- }
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
Output
Else If Statement
It is another decision-making statement. It evaluates the Statement only 'if condition' is true from several conditions, 'elseif statement' can be used many times in a program; if the two conditions are false it means else Statement is executed.
Syntax
- If (condition 1)
- {
- statement 1; //true
- }
- elseif (condition 2)
- {
- statement 2; //true
- }
- else
- {
- statement; //evaluate if condition is false
- }
Example
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>if Condition</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Conditional Statement in JavaScript</h1>
- <script type="text/javascript">
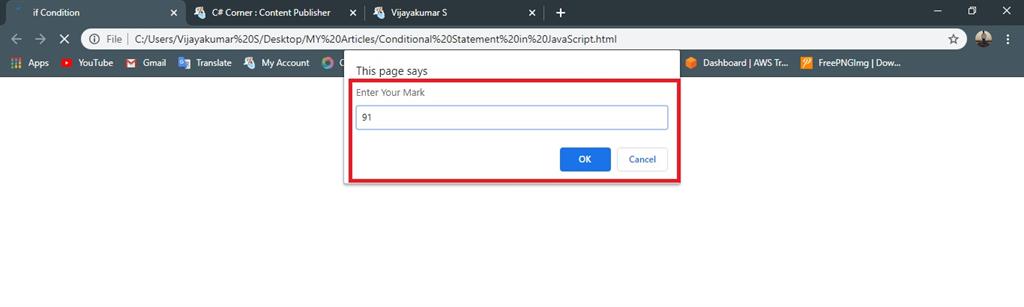
- var mark =(prompt("Enter Your Mark"))
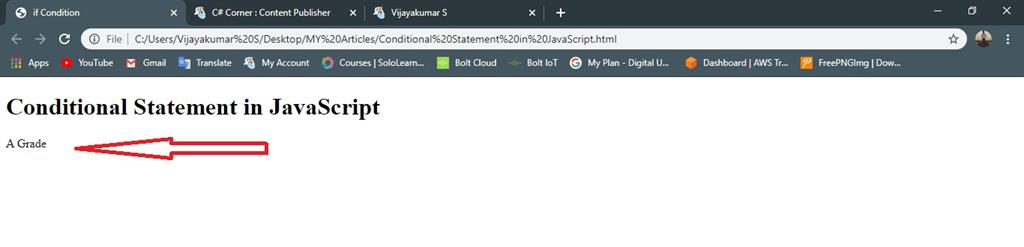
- if (mark>= 90 && mark <=100)
- {
- document.write("A Grade"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
- else if (mark >= 80 && mark <=89)
- {
- document.write("B Grade"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
- else if (mark >= 70 && mark <= 79)
- {
- document.write("C Grade"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
- else if (mark >= 60 && mark <= 69)
- {
- document.write("D Grade"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
- else if (mark >= 35 && mark <= 59)
- {
- document.write("E Grade"); //given condition is true execute the statement
- }
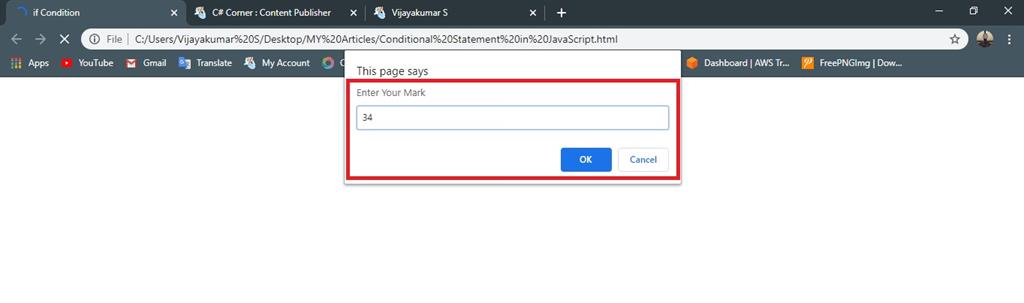
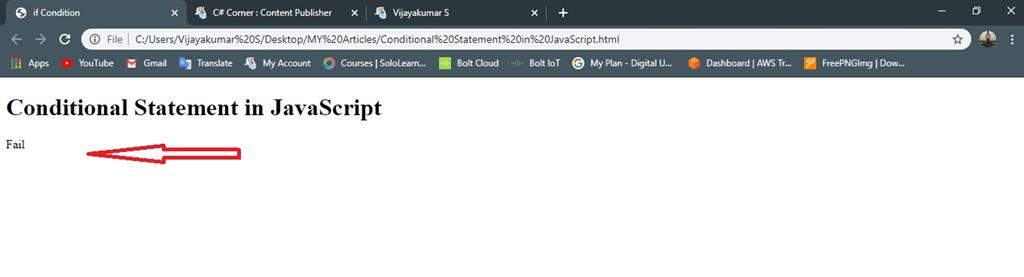
- else
- {
- document.write("Fail"); //given condition is false execute the statement
- }
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
Output
Below 35 mark
Switch Case
Switch Case Statement is a control Statement, it is better than If else statements. To improve the readability of a program multiple if-else Statements can be replaced with Switch Statements. In Switch Case Statements, using the break statement will cause an immediate exit from the switch statement as soon as the code under the code is executed.
Syntax
- Switch (expression){
- Case 1:
- Statement;
- Break;
- Case 2:
- Block of Statement:
- Break:
- Default:
- Block of statement:
- }
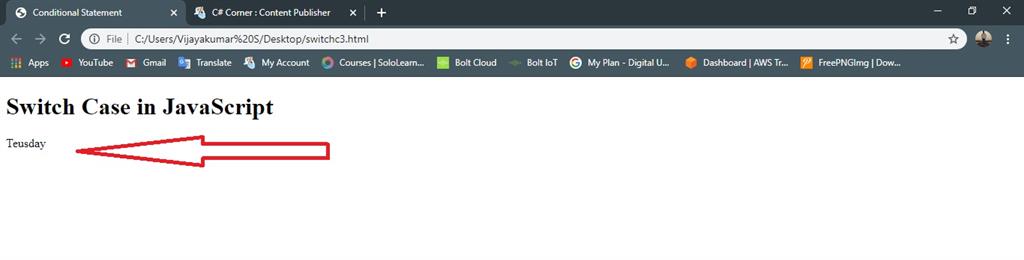
Example
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Conditional Statement</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Switch Case in JavaScript</h1>
- <script type="text/javascript">
- var days = 3;
- switch (days)
- {
- case 1:
- document.write("Sunday");
- break;
- case 2:
- document.write("Monday");
- break;
- case 3:
- document.write("Teusday");
- break;
- case 4:
- document.write("Wednesday");
- break;
- case 5:
- document.write("Thusday");
- break;
- case 6:
- document.write("Friday");
- break;
- case 7:
- document.write("Saturday");
- break;
- default:
- document.write("There is no day");
- break;
- }
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
Output
Summary
In this chapter, we learned about Conditional Statements in JavaScript and how to use these statements with example programs.
Author
Vijayakumar S
0
3.9k
2m
