Internet of Things: Real-World Applications
Introduction
You will consider that some technologies are an essential part of existence.
IoT Real World Applications
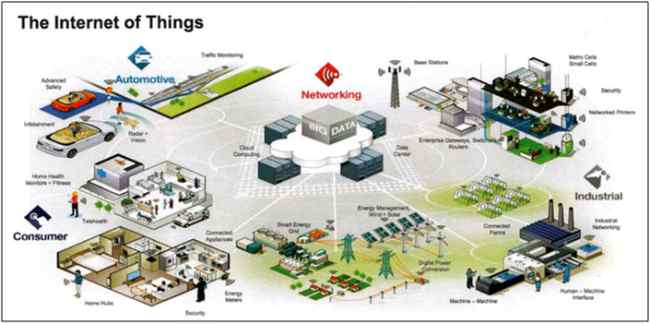
Figure: IoT in every aspect of our lives
Let's look at the way the IoT does this.
Home
The retail stores now have smartphone app-controlled thermostats and lighting solutions. These are also a large range of protections, including remotes, automated monitoring, etc. The system also extends to many other tools and accessories for home use.
- Home security and Access control
- Lighting control
- Home health care
- Fire detection including leak detection
- Energy efficiency
- Solar panel monitoring and control
- Temperature monitoring and HVAC control
- Automated meter reading
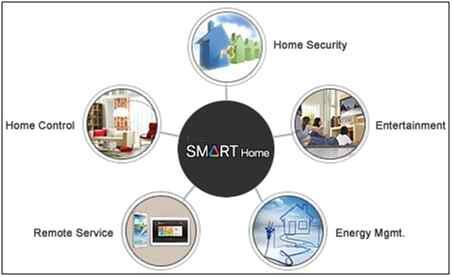
Figure: Smart Home – IoT Application
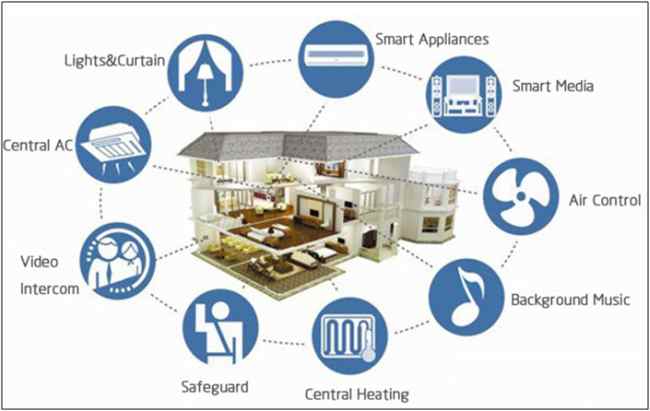
Figure: Use of IoT in every aspect of Smart Home
Healthcare
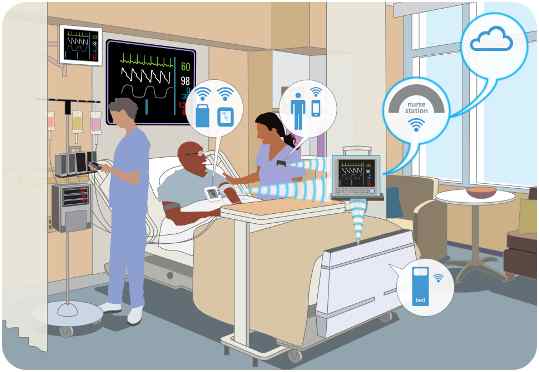
Figure: IoT in Clinical Care
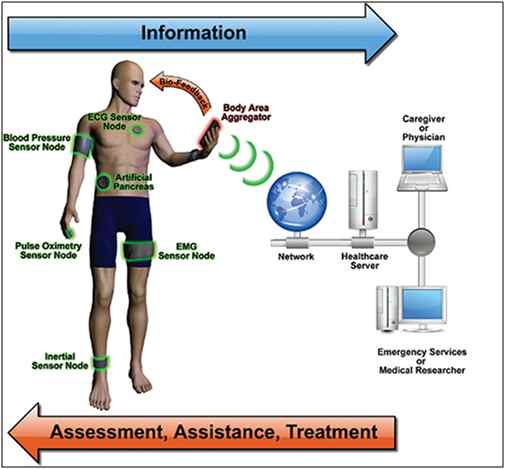
Figure: Sensors connected on a patient for Remote Health Monitoring
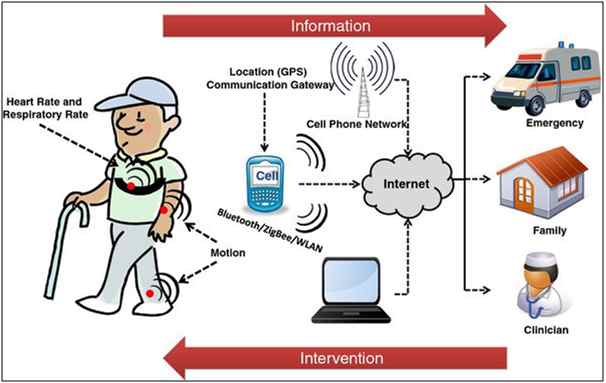
Figure: IoT in Remote Health Monitoring
Smart Energy
- Smart grid: “A smart grid is a modernized
the electrical grid that uses analog or digital information and
communications technology to gather and act on information, such as
information about the behaviors of suppliers and consumers, in an
automated fashion to improve the efficiency, reliability, economics, and
sustainability of the production and distribution of electricity.” –
Wikipedia.
- Smart meter: “A smart meter is usually an electronic device that records consumption of electric energy in intervals of an hour or less and communicates that information at least daily back to the utility for monitoring and billing. Smart meters enable two-way communication between the meter and the central system. Unlike home energy monitors, smart meters can gather data for remote reporting.” – Wikipedia.
With
Smart Energy Metering, not only do technicians not need to come and
physically read your meter, you have access personally to your energy
usage so you can see what impact your consumption patterns have on your
wallet and on the environment.
Reasons for the smart grid:
- Stopping power threat.
- Higher quality/reliability of power, fewer blackouts.
- Efficient energy utilization.
- A smart grid is required for renewable power.
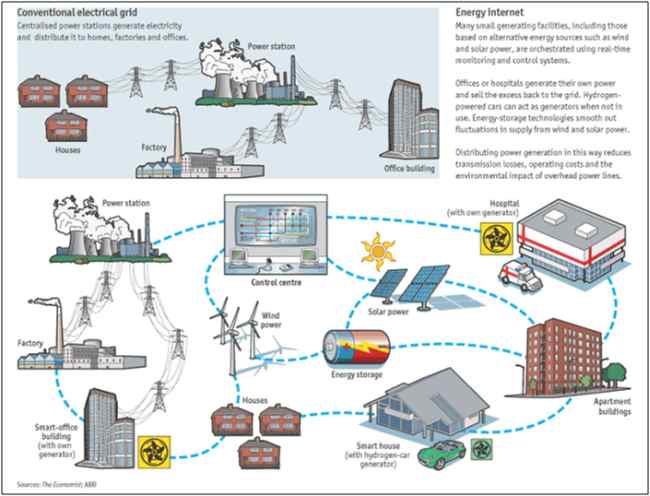
Figure: From conventional grid to Smart Grid
Connected Cars
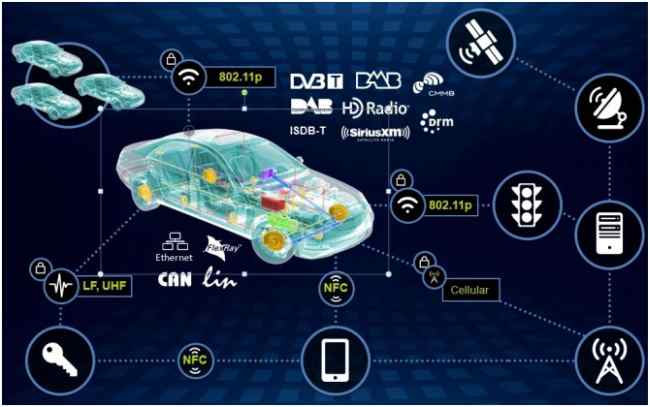
Figure: Connected Car
Environment
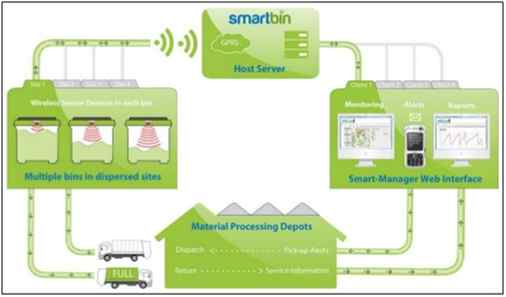
Figure: Smart Waste Management
Cities
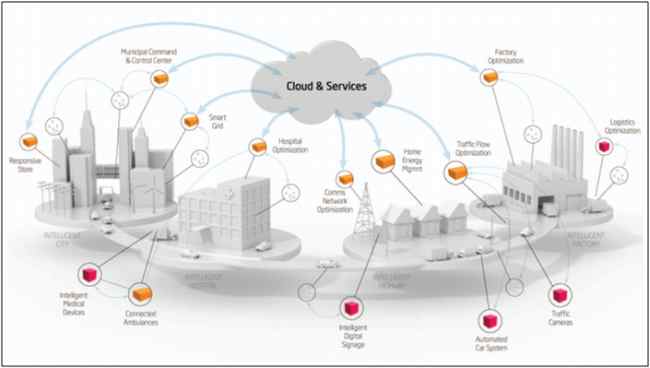
Figure: Smart City with IoT
Business
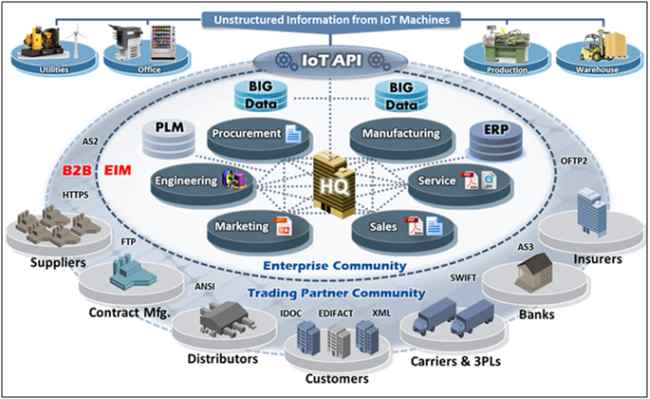
Figure: IoT in Business
Government
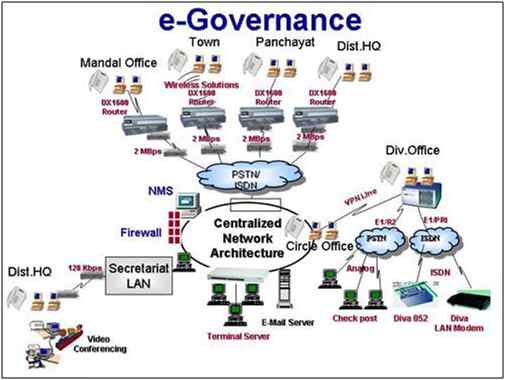
Figure: IoT and Government
Agriculture
- Crop monitoring: Sensors can be used to monitor crops and the health of plants using the data collected. Sensors can also be used for the early monitoring of pests and disease.
- Food safety: The entire supply chain, the Farm, logistics and retails, are all becoming connected. Farm products can be connected with RFID tags, increasing customer confidence.
- Climate monitoring:
Sensors can be used to monitor temperature, humidity, light intensity,
and soil moisture. These data can be sent to the central system to trigger alerts and automate water, air, and crop control.
- Logistics monitoring: Location-based
sensors can be used to track vegetables and other Farm products during transport and storage. This enhances scheduling and automates the supply chain.
- Livestock farming monitoring: The monitoring of Farm animals can be monitored via sensors to detect potential signs of disease. The data can be analyzed from the central system and relevant information can be sent to the farmers.
 Figure: IoT in Agriculture
Figure: IoT in Agriculture
And the list of IoT applications continues.
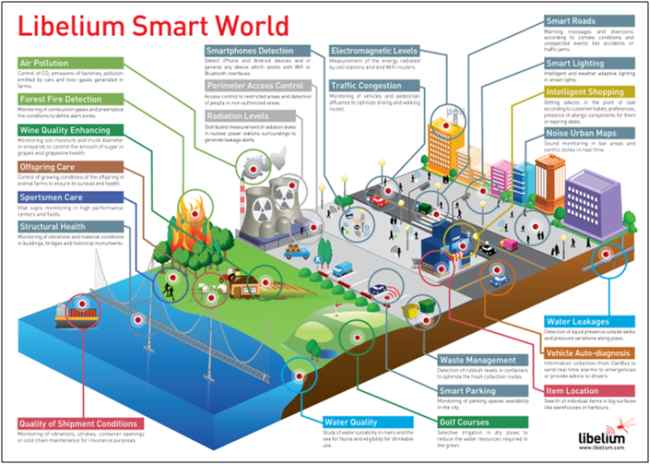
Figure: Numerous IoT Applications
Author
Sukanya Mandal
0
978
620.4k
