Internet of Things: More About Raspberry PI
Introduction
Anatomy of Raspberry Pi
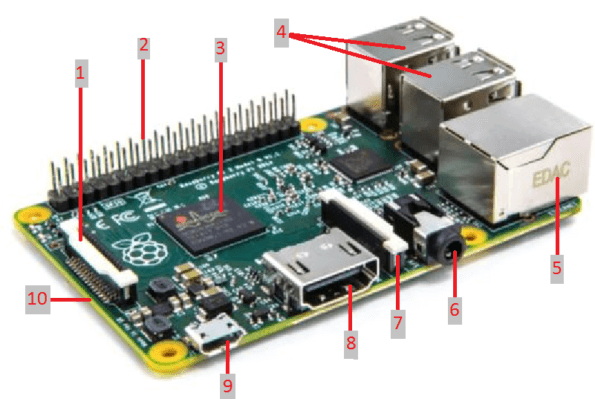
- DSI
The Display Interface (DSI) is used to connect the display directly to the Raspberry Pi board.
- GPIO Pins
These are 40 GPIO (General Purpose Input Output) pins, these pins can be directly accessed on Raspberry Pi. These are used in the projects to connect Raspberry Pi to the electronic circuits, sensors, and control them. These pins can be turned on or off, based on the requirement when the Raspberry is running.
- ARM Processor
It's the heart of the Raspberry Pi, the Broadcom BCM2835 900MHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 CPU with 1GB RAM.
- USB Ports
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports are used to connect the standard accessories such as a keyboard, mouse, Wi-Fi adapter, etc. It has 4 USB ports. (It is recommended to use a powered USB hub to power all the USB devices like keyboard and mouse etc. because powering (connecting) these devices directly to the Raspberry Pi would leave the Pi under-powered, leading to a shorter component life and even nonfunctioning Pi.)
- Ethernet Connection
You can connect Pi to a network or home modem/ router, using an Ethernet cable and the connection. Raspberry Pi 2 Model B does not have a built-in Wi-Fi, but you can add a USB Wi-Fi adapter to the USB port.
- 3.5 MM Audio / Video Jack
This 3.5 mm audio jack is normally used to attach the headphones or the speakers. Raspberry Pi 2 also carries composite video, using a compatible cable.
- CSI (Camera Serial Interface)
This interface is used to attach the Raspberry Pi 1 camera module directly to the motherboard via a CSI connection.
- HDMI
HDMI connection enables you to hook up Raspberry Pi to the most modern Monitors and digital Televisions. It carries both the video and audio. (Note, in case you have old monitors having VGA port, you would need HDMI to VGA port adapter to hook up your Raspberry Pi to the old monitor).
- USB Power
This port is used to power on Pi. You can use a 5V 2000mA Micro USB power supply and compatible cable to power up the Pi.
- Mini SD Card Slot
Raspberry Pi does not have secondary storage. You need to use mini SD cards to store the data and OS. These SD cards with OS need be inserted into the SD card slot before powering up Pi.
That’s all for this chapter. I hope you enjoyed reading!!
Author
Hussain Patel
609
1.8k
546.7k