Internet of Things: Components, Boards and Jumper Wires
Introduction
You've learned everything from IoT, it's software, and its building blocks until now. The next step is to think about IoT technology's hardware component. The IoT is an incredibly wide area, with thousands of modules, boards, and wires being used or created.
It is important to understand the difference between microcontrollers and on-board devices to better understand the concept and get the best from the chapter.
Microcontroller vs. System on Board
IoT Components

Electronic Components
 Raspberry Pi is a very low-cost computer of credit
card size, by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. The Raspberry Pi Foundation
is a registered educational charity in the UK.
Features of Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi is a very low-cost computer of credit
card size, by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. The Raspberry Pi Foundation
is a registered educational charity in the UK.
Features of Raspberry Pi
- RED LED
- GREEN LED
- Resistors
- Capacitor
- Push-button
- Male breakable header strip
- Break Away Headers - Straight
Power Options
- 5V Power adapter with a micro USB cable
- Power Banks
- Polymer Lithium-Ion Battery
- Flexible 6V 1W Solar Panel
- Solar Charger Shield
- Voltage Regulator
Micro SD Card
8GB/ 16GB /32GB class 10 microSD card with NOOBS pre-installed
Note: For 64 GB, please check the list of supported devices.
Other Components
Breadboards, ProtoPi NifTee, Raspberry Pi Case, HDMI cables, etc.

IoT Boards
Raspberry Pi
- Low cost: starting from $5
- Compact size: credit card sized
- Connect your monitor/TV:
- You can directly connect your Raspberry Pi with your monitor or TV, using HDMI port.
- If you have an old monitor that doesn’t have HDMI port, then, you can use HDMI to VGA cable for that.
- Connect Standard Mouse and Keyboard:
- If you have a wireless keyboard, you can connect it using Bluetooth.
- Connect your wired keyboard/ mouse using the USB port.
- Use USB to PS2 converter cable for connecting your PS2 mouse/keyboard.
- Beneficial for exploring computing, by people of all ages. We can do a lot of things with it. We can play games, work with spreadsheet software, play HD video, internet surfing, and many more things.
- We can use it for exploring the Internet of Things. We can write programming for it in different types of languages. Being a Microsoft technology developer, I’ll prefer coding in C#, but it also supports C++, Java, Python, Node JS, Ruby, etc. For IoT, Raspberry Pi 3 can be used in different ways. We can do a lot of things using Pi.
There are 5 models available on the official website of Raspberry pi. Those Models are,
- Raspberry Pi Zero
- Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+
- Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+
- Raspberry Pi 2 Model B
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B
I
am not going to explain all the devices, but I can put a layout
of Raspberry Pi Zero and Raspberry Pi 3 Model B so that you can
understand very easily what changes are done and what is the difference
between the first Raspberry Pi (Raspberry Pi Zero) and the latest
Raspberry Pi (Raspberry Pi 3 Model B)
 Many of us are familiar with Intel boards and
processors for our PC and laptop. We know that Intel is a leading
manufacturer of CPU and boards. Intel has developed some boards which
can be used for IoT development.
Many of us are familiar with Intel boards and
processors for our PC and laptop. We know that Intel is a leading
manufacturer of CPU and boards. Intel has developed some boards which
can be used for IoT development.
 There are different versions of Intel Galileo e.g. Intel Galileo Gen. 1,
Intel Galileo Gen. 2, etc. If you are interested in Intel Galileo, you
can explore it.
There are different versions of Intel Galileo e.g. Intel Galileo Gen. 1,
Intel Galileo Gen. 2, etc. If you are interested in Intel Galileo, you
can explore it.
 You can explore a complete list of Arduino boards for the Internet of Things, here.
Netduino is .NET-programmable microcontroller which is available in different models. Some of them are:
You can explore a complete list of Arduino boards for the Internet of Things, here.
Netduino is .NET-programmable microcontroller which is available in different models. Some of them are:
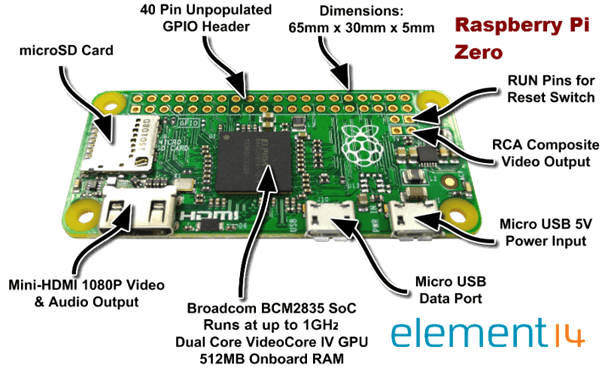
Raspberry Pi Zero

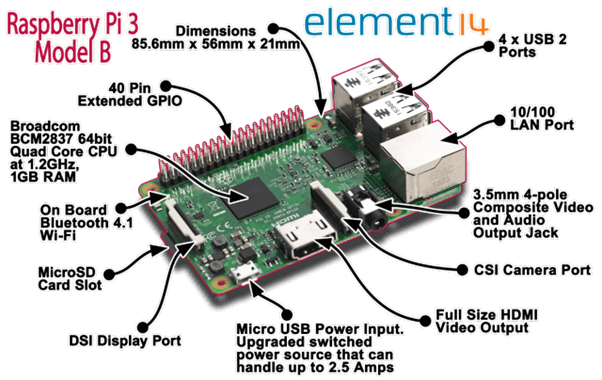
Raspberry Pi 3

Image Source: www.element14.com
IoT Devices from Intel
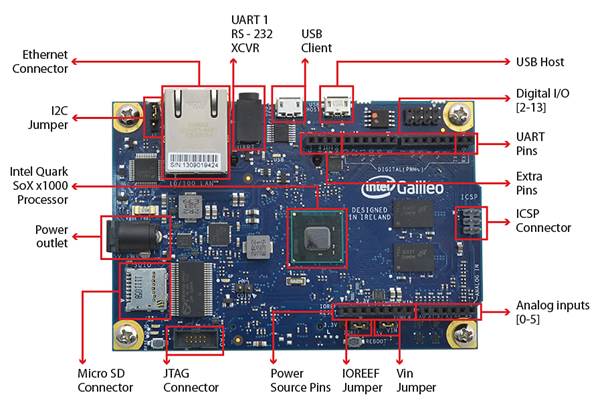
Intel® Galileo

Image Source: https://www.cooking-hacks.com
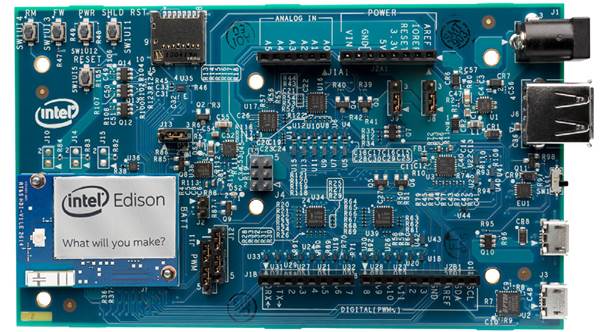
Intel Edison

Arduino

Netduino
- netduino (.NET-programmable microcontroller)
- netduino Plus (.NET-programmable microcontroller with Ethernet)
- netduino 2 (.NET-programmable microcontroller)
- netduino Plus 2 (.NET-programmable microcontroller)
- netduino 3
- netduino 3 Ethernet
- netduino 3 Wi-Fi (.NET-programmable microcontroller)

The above Image is for netduino 3 Wi-Fi which is the latest version of netduino board.

We use jumper wires with IoT boards,
like Raspberry Pi 3, for connecting devices, so that we can write and
execute our code which can be used to pass power and data using GPIO
port.
Jumper wires come in different categories and styles. Please make your correct selection depending on your requirements.
Single wired
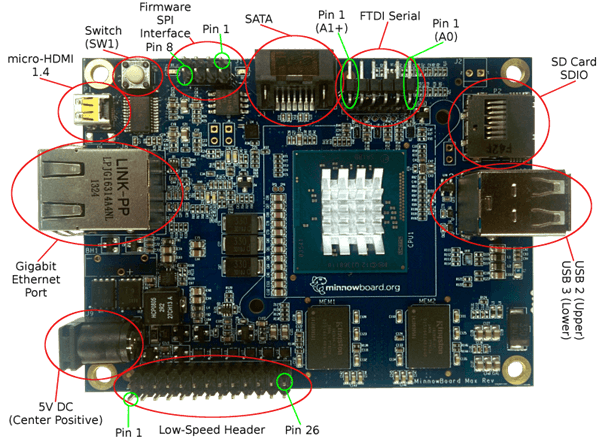
Minnow Board MAX


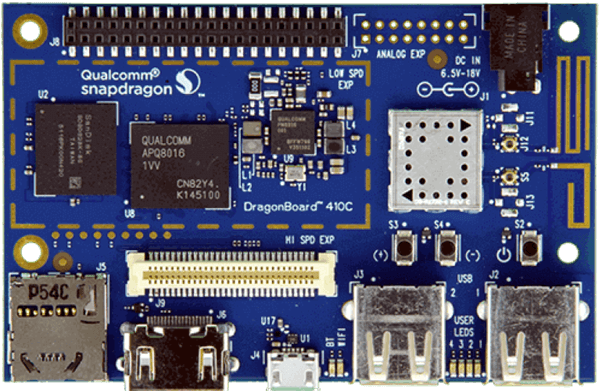
Qualcomm Dragon Board™ 410c

Jumper Wires
Types of Jumper wire
- Male to Male jumper wire
- Male to Female jumper wire
- Female to Female jumper wire
24 pins/ 40 pins jumper wires
- Male to Male 24 pins/40 pins jumper wire
- Male to Female 24 pins/40 pins jumper wire
- Female to Female 24 pins/40 pins jumper wire
40 pins jumper wires can also be detached separately and we can use it as separate 40 jumper wires.
That is all for this chapter. I hope you enjoyed reading it!
Author
Banketeshvar Narayan
121
15.8k
5.8m
