I encountered below error message when profiling an Winforms based vb.net Application using RedGate Profiler..
It is related to memory access violation. My Local code instance crashed soon after I clicked 'F5' from Visual Studio Code. 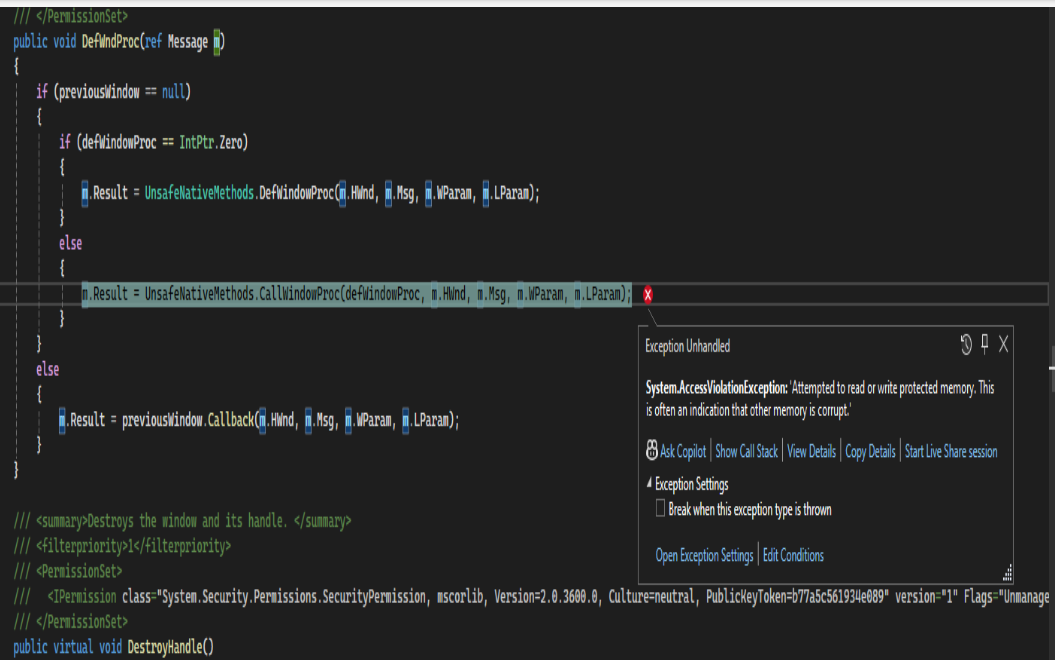
The System.AccessViolationException : "Attempted to read or write protected memory. This is often an indication that other memory is corrupt." It is a system file "NativeWindow.cs" from where this exception occured..
Any one having any idea on how this particular error can be resolved ?