|
|
|
|
|
Similar ArticlesMost ReadTop RatedLatest
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
A DataRow represent a row of data in data table. You add data to the data table using DataRow object. A DataRowCollection object represents a collection of data rows of a data table. You use DataTable's NewRow method to return a DataRow object of data table, add values to the data row and add a row to the data Table again by using DataRowCollection's Add method.
Before adding rows to a data table, I'll discuss the DataRow class properties and methods. Table 1 describes DataRow class properties, and Table 2 describes the DataRow class methods.
Table 1: The Data Row Class properties
|
PROPERTY |
DESCRIPITION |
|
Item |
Represents an item of a row |
|
ItemArray |
Represents all values in a row |
|
RowState |
Indicates the current state of a row |
|
Table |
Returns the DataTable to which this row is attached |
Table 2: The Data Row class Methods
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|
AcceptChanges |
Comments all the changes made to this row |
|
BeginEdit |
Starts an edit operation on a row |
|
CancelEdit |
Cancels the current edit on a row |
|
Delete |
Deletes a DataRow |
|
EndEdit |
Ends the current edit on a row |
|
GetChildRows |
Returns child rows of a DataRow |
|
GetParentRows |
Returns parent rows of a DataRow |
|
RejectsChanges |
Rejects all the changes made since last AcceptChanges |
You access DataRow members through the table column. A column acts as item of the row. For example, if a data table has three columns such as Id, Name, and Address, then a row will have three members; Id, Name, and Address. You access data row members using the name of columns. For example, listing below sets value of the Id, Name, and Address Columns.
Listing: Setting values of the Id, Address, and Name Columns of a DataRow
DataRow row1 = custTable.NewRow();
row1["id"] = 1001;
row1["Address"] = "43 Lane wood Road, Cito, ca";
row1["Name"] = "George Bishop";
After setting a row member's values, you call DataTable's DataRowCollection's Add method though the DataTable.Rows property to add a row to the data table:
custTable.Rows.Add(row1);
The RejectChanges method of the DataRow rejects recent changes on that row. For Example, if you have recently added row1 to the data table, calling the RejectChanges method as following:
row1.RejectChanges();
Won't add the row to the data table.
You can also delete a recently added row to a data table by calling DataRow's Delete method:
Row1.Delete();
CAUTION RejectChanges and Delete method may not work together if you're applying both methods on the same row because RejectChanges doesn't add a row to the data table.
Listing below shows a program that creates a DataTable with three columns (Id, Name, and Address) and adds three rows to the data table. At the end, this program attaches the newly created DataTable to a data grid control using a dataset.
CAUTION As you can see from Listing below, the Id column of the Customers table is read-only (the Read Only property is true). That means you'll not be able to add data to the table. If you want to add data from the front-end, you need to set the ReadOnly property as false.
Listing: Adding rows to a DataTable using DataRow
// This method creates customers table
private void CreateCustomersTable()
{
// Create a new DataTable.
System.Data.DataTable custTable = new DataTable("Customers");
DataColumn dtColumn;
// Create id column
dtColumn = new DataColumn();
dtColumn.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.Int32");
dtColumn.ColumnName = "id";
dtColumn.Caption = "Cust ID";
dtColumn.ReadOnly = true;
dtColumn.Unique = true;
// Add id column to the DataColumnCollection.
custTable.Columns.Add(dtColumn);
// Create Name column.
dtColumn = new DataColumn();
dtColumn.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.String");
dtColumn.ColumnName = "Name";
dtColumn.Caption = "Cust Name";
dtColumn.AutoIncrement = false;
dtColumn.ReadOnly = false;
dtColumn.Unique = false;
// Add Name column to the table.
custTable.Columns.Add(dtColumn);
// Create Address column.
dtColumn = new DataColumn();
dtColumn.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.String");
dtColumn.ColumnName = "Address";
dtColumn.Caption = "Address";
dtColumn.ReadOnly = false;
dtColumn.Unique = false;
// Add Address column to the table.
custTable.Columns.Add(dtColumn);
// Make the ID column the primary key column.
DataColumn[] PrimaryKeyColumns = new DataColumn[1];
PrimaryKeyColumns[0] = custTable.Columns["id"];
custTable.PrimaryKey = PrimaryKeyColumns;
// Instantiate the DataSet variable.
DataSet ds = new DataSet("customers");
// Add the cust Table to the Dataset.
ds.Tables.Add(custTable);
// Add rows to the custTable using its NewRow method
// I added three customers with their addresses, name and id
DataRow row1 = custTable.NewRow();
row1["id"] = 1001;
row1["Address"] = "43 Lane wood Road, cito, CA";
row1["Name"] = " George Bishop";
custTable.Rows.Add(row1);
DataRow row2 = custTable.NewRow();
row2["id"] = 1002;
row2["Name"] = "Rock Joe";
row2["Address"] = "King of Prussia, PA";
custTable.Rows.Add(row2);
DataRow row3 = custTable.NewRow();
row3["id"] = 1003;
row3["Name"] = "Miranda";
row3["Address"] = "279 P. Avenue, Bridgetown, PA";
custTable.Rows.Add(row3);
// row3.RejectChanges( );
// row2.Delete( );
// Bind dataset to the data grid
dataGrid1.DataSource = ds.DefaultViewManager;
}
The output of the program looks like figure below.
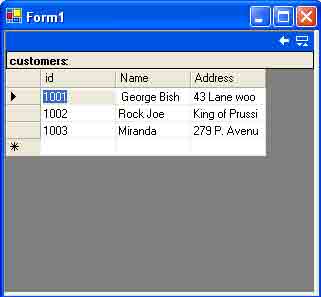
Figure: Adding rows to a Data Table
Note: To run this program, create a Windows application and drop a data grid control on the form. After that you can either call CreateCustomersTable listed in Listing above from the form load or from a button- click handler. You can write a form load event by double-clicking on the form or by opening the properties windows.
If you uncomment the bold lines row3.RejectChanges() and row2.Delete() at the end of listing, shown in Listing above, the output looks Figure below. The RejectChanges method rejects the addition of row 3, and the Delete method deletes row 2.
Listing: Calling DataRow's RejectChanges and Delete methods
private void CreateCustomersTable()
{
// More code . . .
row3.RejectChanges();
row2.Delete();
// Bind dataset to the data grid
dataGrid1.DataSource = ds.DefaultViewManager;
}
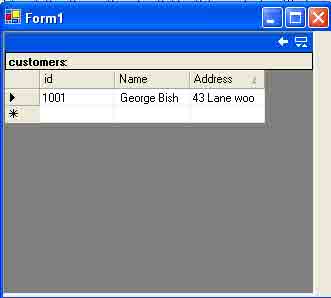
Figure: Result of the RejectChanges and Delete DataRow methods
The DataRowState Enumeration
The DataRowState enumeration returns the current state of a row. It's useful during operations when you want to know the current state of a row. Table below lists the value of the DataRowState enumeration.
Table: The DataRowState Enumeration Members
|
MEMBER |
DESCRIPTION |
|
Added |
Row has been added and AcceptChanges has not been called. |
|
Deleted |
Row was deleted using the Deleted method. |
|
Detached |
Row was created but deleted before it was added to the collection. |
|
Modified |
Row has been modified, but AcceptChanges is not called yet. |
|
Unchanged |
Row has not changed since last AcceptChanges was called. |
The RowState property of a DataRow returns the DataRowState enumeration. You can use this to find out the current state of row. For example, listing below calls RowState just after the Delete and RejectChange methods.
Listing: Calling DataRow's RejectChanges and Delete methods
row3.RejectChanges();
MessageBox.Show(row3.RowState.ToString());
row2.Delete();
MessageBox.Show(row2.RowState.ToString());
Conclusion
Hope this article would have helped you in understanding Data Row in ADO.Net. See my other articles on the website on ADO.NET.
|